Today (25th), the reporter learned from the Institute of High Energy Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences that recently, the research team led by the institute, through the analysis of the joint observation data of the Polar Space Telescope and the Fermi satellite, discovered a gamma-ray spectrum line with an energy of up to 37 MeV in the gamma-ray burst, and the energy and luminosity of the spectrum line evolved in the form of a power law. This is the highest energy and most conclusive spectrum line produced by celestial bodies observed so far. These discoveries provide new and important clues to solve the mystery of gamma-ray bursts and relativistic jets, and are a milestone in the observation and research of gamma-ray bursts. The relevant research results were officially published in the journal "Science China: Physics, Mechanics and Astronomy" (English version) as a cover article on July 25.

△This research result was published as a cover article in Science China: Physics, Mechanics and Astronomy (English edition). The picture shows the observation of the brightest gamma-ray burst to date by the Polaris Space Telescope and the Fermi satellite, and the joint discovery of the gamma-ray spectrum lines evolving over time.
In this study, the "Huairou-1" Polaris satellite team of the Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with researchers from the Yunnan Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hebei Normal University, Guizhou Normal University and other institutions, used the observation data of the independently developed Polaris Space Telescope (GECAM-C) and the international Fermi Satellite Gamma-ray Monitor (Fermi/GBM) to carry out detailed energy spectrum analysis and spectral line search for the brightest gamma-ray burst to date. In particular, the precise measurement data of the Polaris Space Telescope were used to calibrate and verify the data of the Fermi satellite, and a large amount of detector background research and instrument effect analysis were carried out, successfully extracting an accurate and reliable gamma-ray burst energy spectrum.
After rigorous analysis, the research team found that there is an emission line spectrum with an evolutionary law in the energy spectrum of the gamma-ray burst. The energy and luminosity of the spectrum line evolve in a power law over time, providing the most solid evidence for the authenticity of the spectrum line and that the spectrum line originated from the gamma-ray burst. In addition, the research team also found that the relative broadening of the spectrum line is narrow (only about 10%) and basically does not change with time. What is even more surprising is that during the main burst phase of the gamma-ray burst, the energy of the spectrum line is as high as 37 MeV, which is the highest energy spectrum line produced by cosmic objects detected so far. These findings are of great and unique value for studying the physical properties and generation mechanisms of gamma-ray bursts and relativistic jets, and are a major breakthrough in the observation and study of gamma-ray bursts and extreme universes.
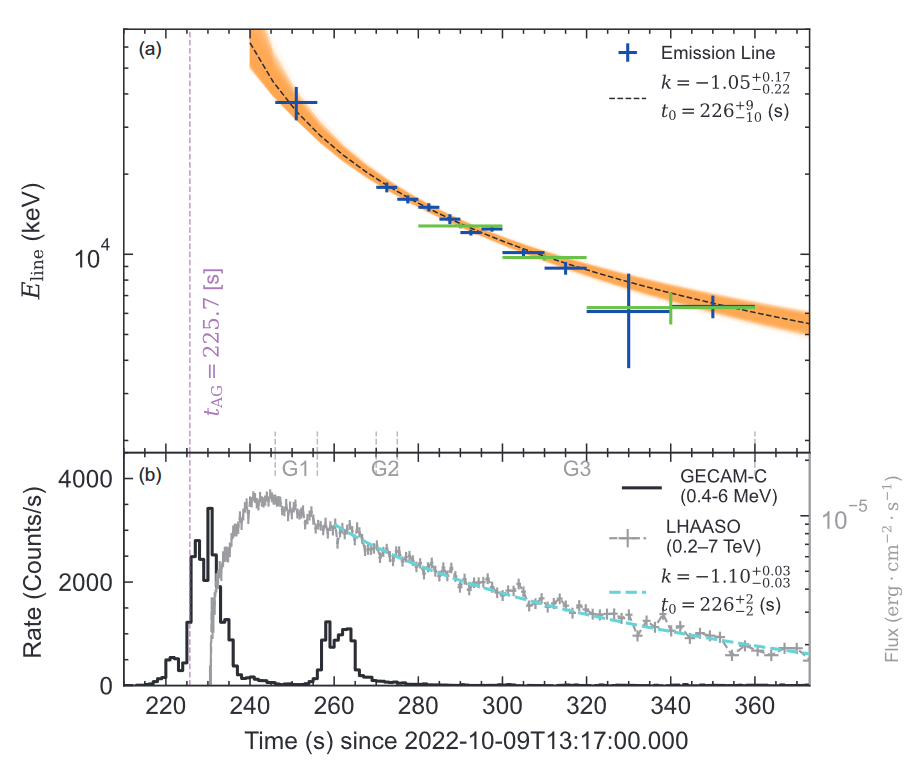
△The research team found that the spectral line energy of the gamma-ray burst evolves according to a power law over time (quoted from the paper of this study).
Gamma-ray bursts are the most violent explosions after the Big Bang. They are generally believed to be produced by the core collapse of massive stars or the merger of two extremely dense celestial bodies (neutron stars, black holes, etc.). Since its first discovery in the 1960s, the observation and research of gamma-ray bursts has always been at the forefront. In particular, with the discovery of gravitational waves in recent years, gamma-ray bursts have become the focus of multi-band multi-messenger time-domain astronomical research. In recent years, my country has launched a series of space telescopes to carry out gamma-ray burst observation and research, including the Insight-HXMT satellite, the Huairou-1 Polaris series of satellites, the Einstein probe satellite, and the Sino-French astronomical satellite. On October 9, 2022, many astronomical telescopes around the world observed the brightest gamma-ray burst to date (numbered GRB 221009A). Among them, my country's Insight-HXMT satellite and Polaris space telescope made precise measurements of the instantaneous radiation of the gamma-ray burst and found that the gamma-ray burst had record-breaking observed brightness and isotropic energy. These extreme properties make it a veritable once-in-a-millennium historical astronomical event.
The "Huairou-1" Polaris satellite (GECAM for short) is my country's first opportunistic space science project supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences' "Space Science" (Phase II) Strategic Priority Research Program. It was launched and put into operation on December 10, 2020. The Polaris Space Telescope (code GECAM-C) involved in this discovery is the third payload of the Polaris series of satellites. It was launched into orbit on July 27, 2022 on the Space New Technology Experimental Satellite led by the Institute of Microsatellite Innovation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The Polaris series of satellites have discovered a large number of high-energy explosion phenomena such as gamma-ray bursts, magnetar bursts, high-energy counterparts of fast radio bursts, solar flares, and terrestrial gamma-ray flashes. The Polaris series of satellites adopts a series of innovative detection technologies, and pioneered the use of the short message service of the Beidou satellite navigation system to achieve quasi-real-time communication between the satellite and the ground, which has revolutionized the use of space telescopes and greatly improved the output of scientific results.