A number of space experiments on the Chinese space station are being carried out in an orderly manner
At present, the third module of the Chinese space station has deployed scientific experiment cabinets in various scientific research fields to support the space station to carry out larger-scale space research experiments and new technology experiments. The reporter learned from the Space Application Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, which is responsible for space station orbit experiments, that the scientific experiment cabinets of the Chinese space station have basically been debugged, and various space experiments are being carried out in an orderly manner.
The variable gravity experiment cabinet has launched lunar and Mars gravity experiments
CCTV reporter Shuai Junquan: What we see on the screen is the experimental picture of the variable gravity scientific experiment cabinet. This is the simulated boiling experiment under the Martian gravity conditions, and the picture next to it is actually a simulated close Particle vibration experiments under zero-gravity conditions.
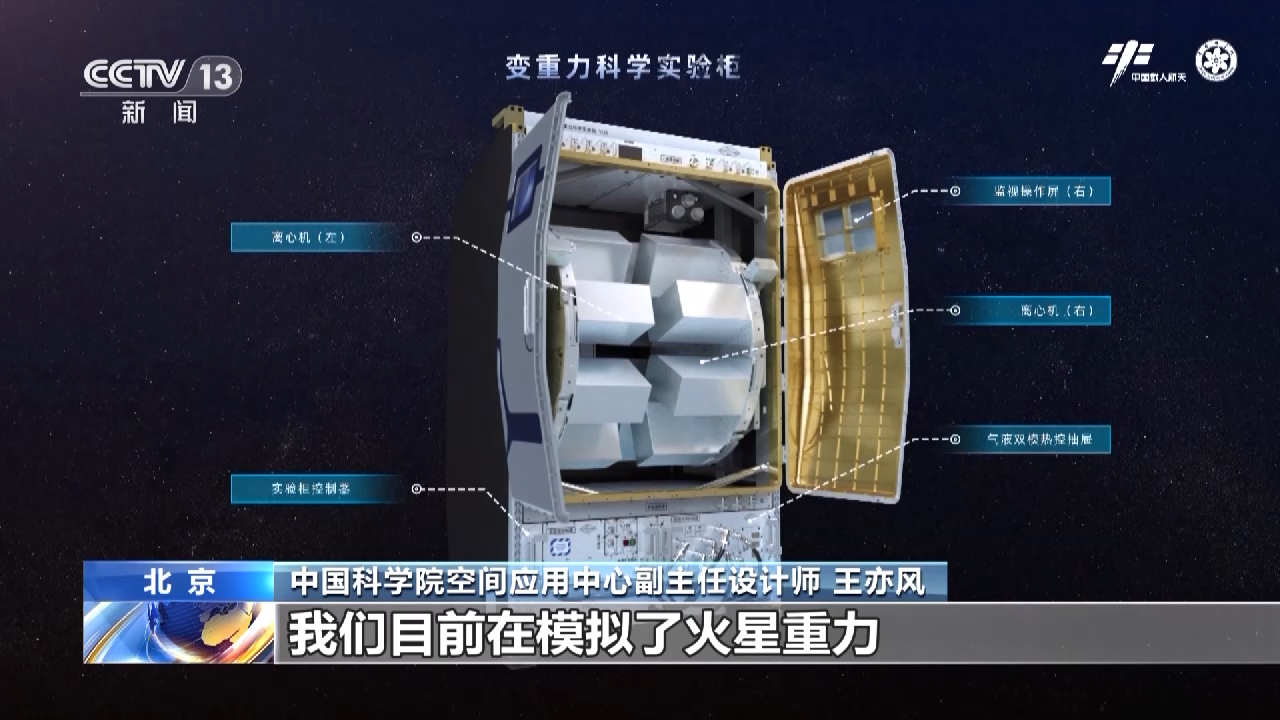
Wang Yifeng, deputy chief designer of the Space Application Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences: In a variable gravity environment of 0~2G, relevant experiments are carried out through the environment provided by our variable gravity scientific experiment cabinet. At present, we have carried out conventional boiling experiments and boiling experiments with limited bubbles under simulated Martian gravity and lunar gravity, and have carried out related research.
In addition, the variable gravity experimental cabinet also carried out research on the vibration fluidization characteristics of granular materials at five low gravity levels, observed the free state of the particle system at a gravity level close to 0G, and the typical state of particle movement at a gravity level of 0~2G. With the assistance of the Shenzhou 15 crew, the scientific research team also carried out combustion science experiments, high-temperature material sample experiments, and fluid physics experiments.

Wang Yifeng, deputy chief designer of the Space Application Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences: The high-temperature material experiment cabinet has carried out high-temperature heating of 5 material samples in orbit, and it will be brought back to the ground for further research with the return of the Shenzhou 15 crew. .
Human pluripotent stem cell space experiment made new progress
Human pluripotent stem cells are an excellent source of cells for regenerative medicine because of their unlimited proliferation potential and ability to differentiate into almost all cell types in the human body. What happens when human pluripotent stem cells grow in space? This is one of the hotspots of current space life science research, and it is also a space experiment being carried out by the Chinese space station.
my country achieves early hematopoiesis from human stem cells in space for the first time
Following the successful launch and docking of Tianzhou 6, the crew of Shenzhou 15 has assisted the scientific research team to start a 6 to 15-day in-orbit cell culture experiment, including the first international human pluripotent stem cell in-orbit experiment. In vitro hematopoietic differentiation of human embryonic stem cells under space conditions.
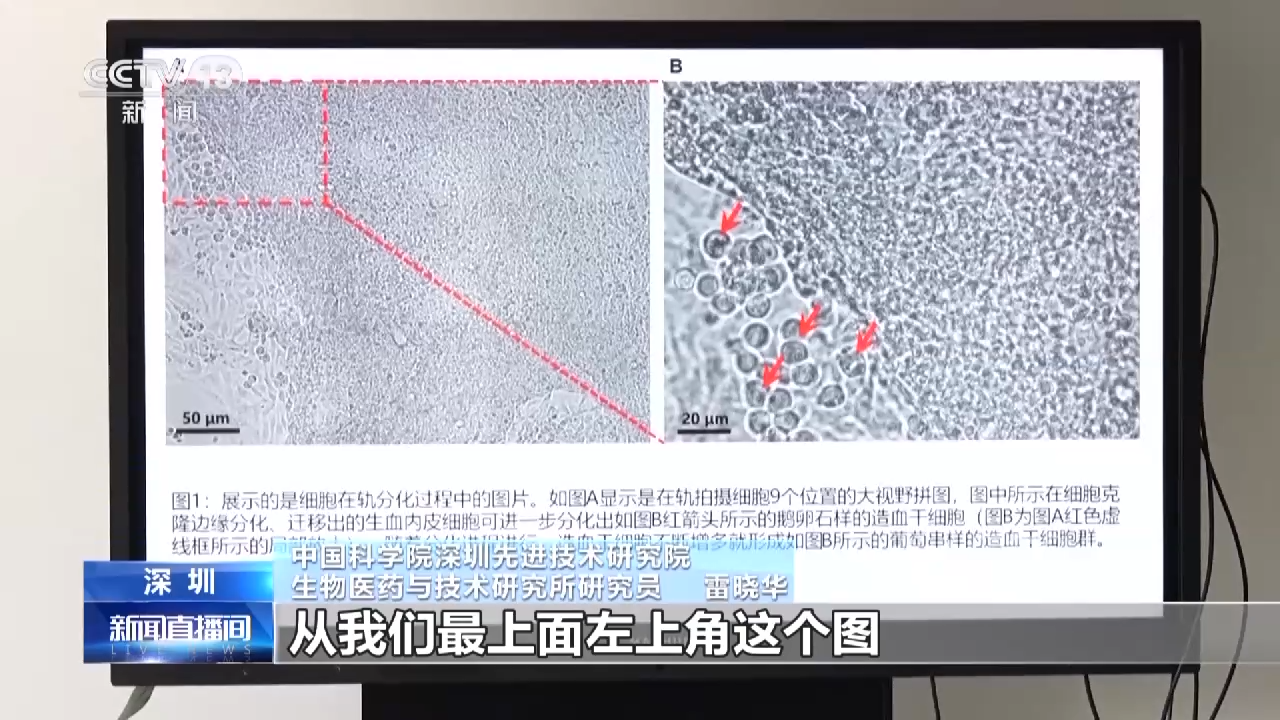
Lei Xiaohua, a researcher at the Institute of Biomedicine and Technology, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences: From the picture in the upper left corner of our top, we can see that in fact we have differentiated into a hematopoietic stem cell similar to a pebble in orbit, so these Hematopoietic stem cells will go through further maturation and differentiation, a group of hematopoietic stem cells similar to a bunch of grapes. In fact, we have achieved the first experimental goal in this experiment, which is the first space hematopoiesis of human stem cells.

In 2017, the scientific research team used the Tianzhou-1 cargo spacecraft to carry out research on the proliferation and differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. The results showed that the space microgravity environment provided very favorable conditions for the 3D growth and stemness maintenance of mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem cells cultured in space exhibit a better 3D growth pattern than the ground and maintain a higher level of pluripotent gene expression. In recent years, foreign scientists have repeatedly reported the use of stem cell growth and tissue regeneration in space missions, such as blood stem cells for astronaut anemia. According to experts, using the unique space microgravity environment may be a new way to solve the problem of maintaining undifferentiated proliferation of stem cells, enhancing the efficiency of induction of differentiation, and improving the level of three-dimensional tissue construction. What a helpful help.

Lei Xiaohua, a researcher at the Institute of Biomedicine and Technology, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Actually, there is still a lot of work to be done. We will also receive a cell sample that we fixed on orbit from the general department of the Space Application Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Then After cryogenically refrigerated and transported back to the laboratory, we need to conduct a comprehensive detection and analysis, and conduct a comparison with the ground control group to screen out the genes related to the space environment affecting the early hematopoietic differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells. In the future, we will use the opportunity of Tianzhou-7 or Tianzhou-8 spacecraft to continue to carry out research on the three-dimensional growth of induced pluripotent stem cells in a space environment, to explore the law of three-dimensional growth of stem cells in a space environment, and the impact of microgravity on stem cells. One mechanism of action for growth effects.
