
For their contributions in click chemistry and bioorthogonal chemistry, American chemist Carolyn R. Bertozzi, Danish chemist Morten Meldal and American chemist Carl K. Barry Sharpless has been awarded the 2022 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
What is click chemistry?
According to the official website of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, click chemistry is a synthetic concept initially proposed by Sharpless in 1998 and gradually perfected thereafter. Its core concept is that synthetic chemistry should be guided by molecular functions, and the chemical synthesis of various molecules should be completed quickly and reliably through the simple splicing of small units.
Based on the concept of click chemistry, the Sharpless team discovered two most representative reactions in 2002 and 2014, respectively: azide-terminal alkyne cycloaddition reaction (CuAAC) catalyzed by monovalent copper ions and six Valence sulfur-fluorine exchange reaction (SuFEx).
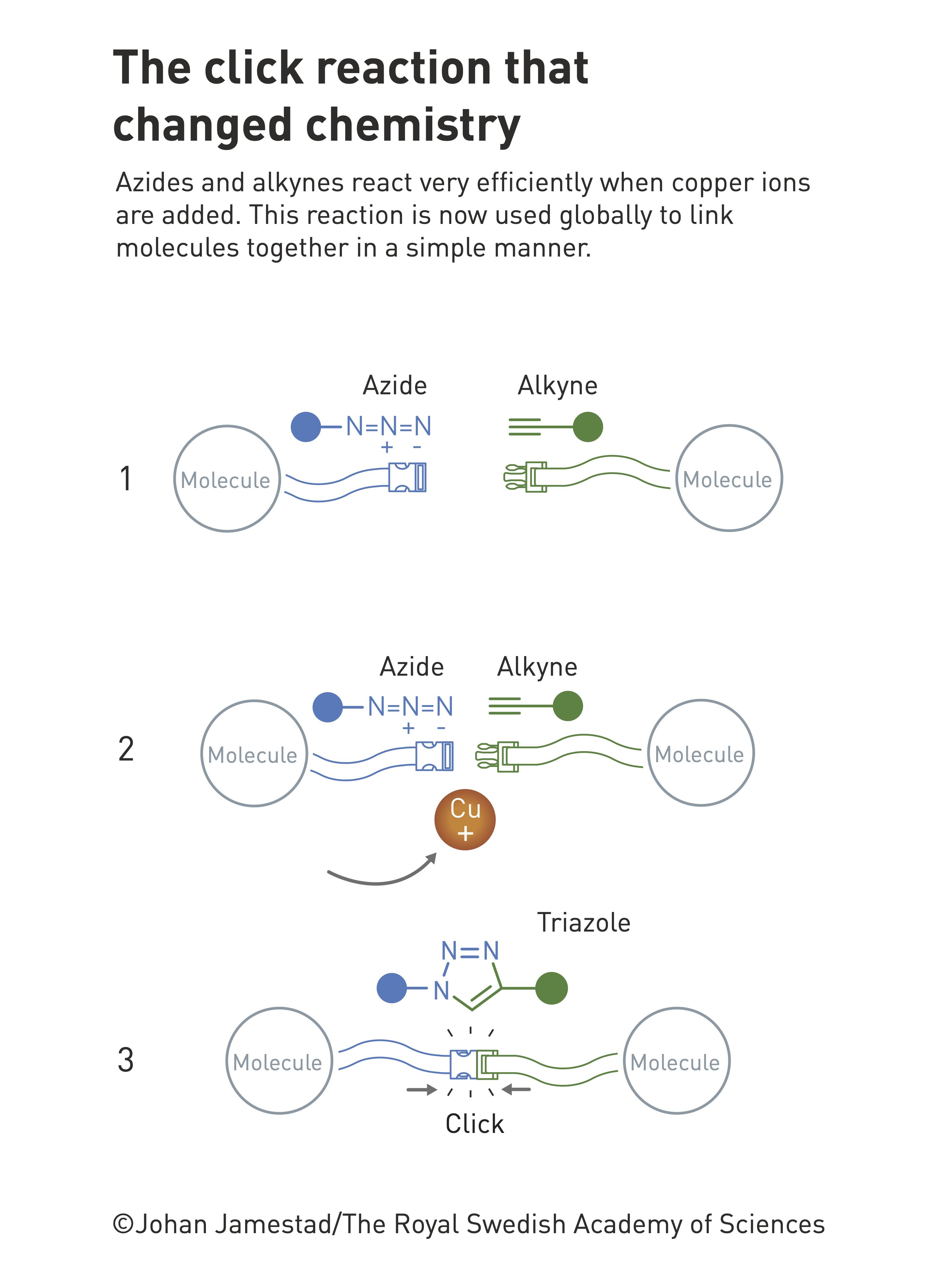
Copper ion-catalyzed azide-terminated alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC)
Click chemistry is one of the most useful and compelling synthetic concepts at present, which has greatly promoted the development of materials chemistry, chemical biology, medicinal chemistry, supramolecular chemistry and other fields.
For Sharpless's outstanding contributions to asymmetric catalysis, especially click chemistry, the 2019 American Chemical Society awarded the Priestley Medal, the highest honor awarded by the American Chemical Society.
According to the aforementioned information on the official website of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, for more than 30 years, Sharpless has maintained close exchanges with Chinese scientists, maintained in-depth cooperation with Chinese universities and research institutes, and has been paying attention to and supporting the development of China's chemical industry. Several generations of Chinese organic chemists have established profound friendships and cultivated a group of outstanding talents for China. Especially since 2016, Professor Sharpless has signed a Distinguished Professor Agreement with the Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and established an independent "click chemistry" laboratory to carry out unique organic fluorine click chemistry research. In just three years, his team has made a breakthrough in the rapid synthesis of azide molecules.
Sharpless was awarded the title of "Honorary Fellow of the Chinese Chemical Society" in 2017 in view of his important contributions to promoting the cooperation between the Chinese chemical community and the international community.
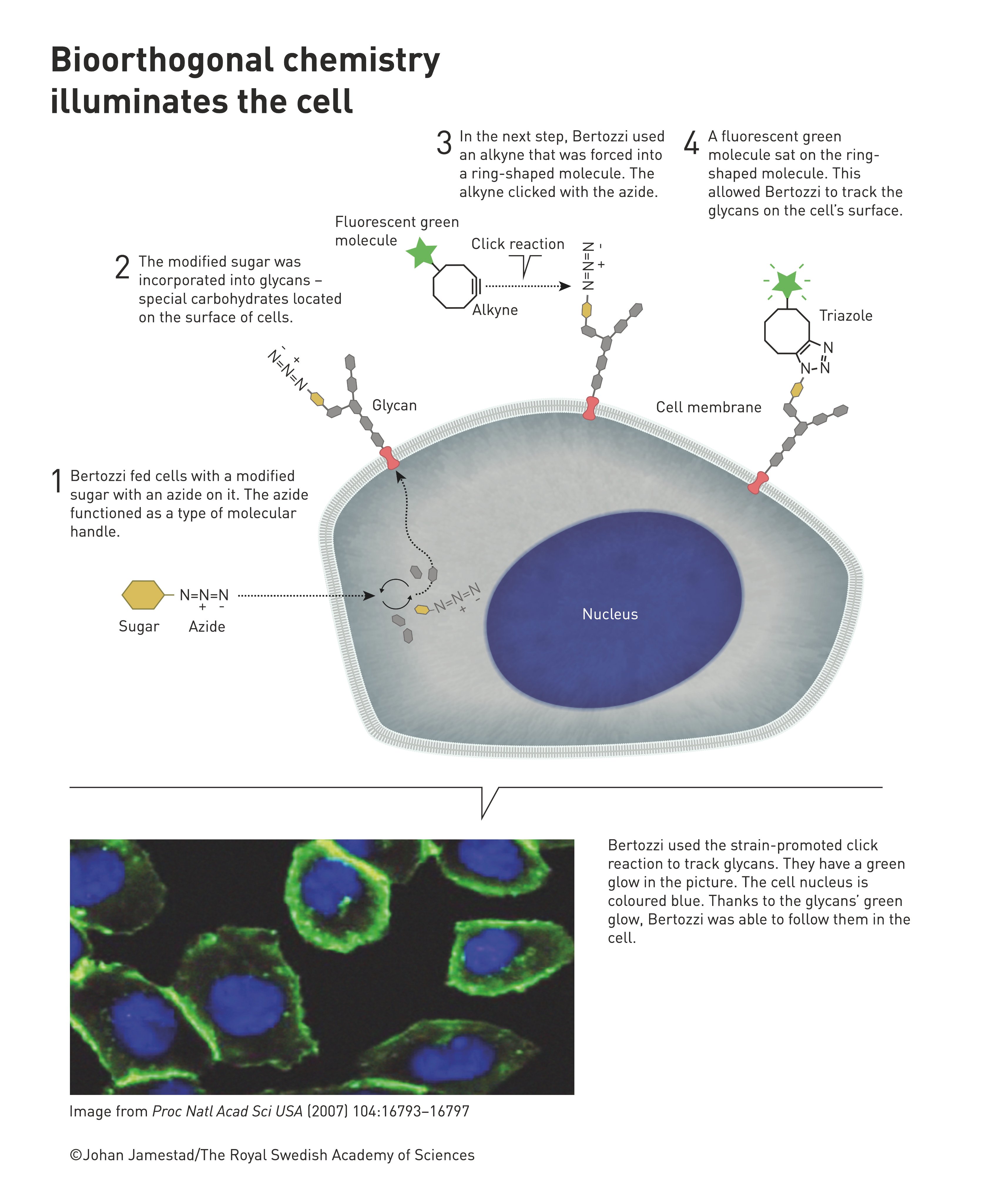
Bioorthogonal chemistry illuminates cells. It does not disrupt the normal chemical reactions of cells.
According to the official website of the Nobel Prize, American chemist Caroline Bertosi took click chemistry to a new dimension and began to use it in living organisms without disrupting the normal chemical reactions of cells. Bioorthogonal chemistry illuminates cells.
What is bioorthogonal chemistry?
According to a paper published in the Journal of Chemistry in 2021 by Fan Xinyuan, an associate professor at the Beijing National Research Center for Molecular Sciences and the School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering at Peking University, bioorthogonal chemical reactions refer to those that can be carried out in biological systems without interacting with natural organisms. A class of chemical reactions in which chemical processes interfere with each other.

Caroline Bertosi's selfie after winning the Nobel Prize in Chemistry on October 5
In 2000, Caroline Bertosi's research group developed the Staudinger coupling reaction based on the Staudinger reduction reaction, the azide-phosphino ester reaction, and used it for chemical modification of the cell surface. Since then, the research upsurge of bioorthogonal reaction has gradually started.
The initial bioorthogonal reaction mainly refers to the coupling reaction, which is used to label, trace, enrich or modify the target biomolecules in the complex environment of the organism.
After more than ten years of development, more than ten bioorthogonal reactions in living cells have been discovered or developed, and these reactions have played an important role in researches such as live cell imaging, biomic analysis, disease diagnosis, and drug development. showed great potential.

2022 Nobel Laureates in Chemistry: American chemist Carolyn R. Bertozzi, Danish chemist Morten Meldal and American chemist Carl Barry Sharpless (K. Barry Sharpless)
According to the paper, the emergence of bioorthogonal chemical reactions has brought revolutionary technology to scientists' in situ research on life processes, and has become one of the core directions of the emerging cross-cutting field of chemical biology. In the nearly 20 years since the concept was proposed, bioorthogonal chemistry has experienced a change in the type of reaction from a single "coupling reaction" to a combination of bond-forming coupling and bond-breaking cleavage reactions, and application scenarios have changed from simple living cell systems to A series of developmental processes for the upgrading of more complex living organisms. At the same time, it has shown broad application prospects in many fields such as life science research, pharmaceutical research and development, and clinical diagnosis and treatment.
