
On August 27, at the Second China Space Science Conference in Taiyuan, researchers from the National Astronomical Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences released the first in-orbit measurement results of the EP-WXT pathfinder. The device is an experimental module of the Einstein Probe (EP) satellite's Wide Field X-ray Telescope (WXT), which was launched on July 27, 2022, Beijing time, with a new space technology test satellite. The purpose of this experiment is to carry out a series of on-orbit tests and observation experiments to lay the foundation for the early scientific operation of future EP satellites. 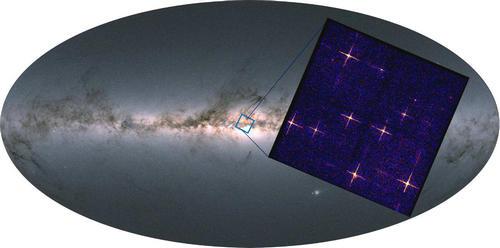
X-ray images obtained from a single observation of the central sky region of the Milky Way by the Widefield X-ray Telescope module
The instrument adopts advanced micro-hole lobster eye X-ray focusing imaging technology, and the observation field can reach 340 square degrees. It is the first wide-field X-ray focusing imaging telescope in the world. Compared with other X-ray focusing imaging telescopes in the world, its field of view is increased by about 100 times. Up to now, the instrument has carried out a four-day on-orbit test observation, and successfully obtained a batch of real X-ray measured images and energy spectra of celestial objects. This is the first wide-field X-ray focused imaging sky map obtained and publicly released in the world. 
X-ray image (left) and simulated image (right) obtained from a single observation of the central sky region of the Milky Way
Scientists used the instrument to first observe the central sky region of the Milky Way. The results show that a single observation can simultaneously detect X-ray sources in multiple directions, including stellar-mass black holes and neutron stars. The observations also captured a neutron star X-ray binary whose X-ray emission was several times brighter. At the same time, the information of the time-varying X-ray radiation intensity of these celestial objects, as well as the X-ray energy spectrum of the celestial objects, can also be obtained from the data. The observed results are in good agreement with the simulation results. The instrument also observed the Milky Way's nearest neighbor, the Large Magellanic Cloud, covering the entire galaxy in a single observation, while detecting multiple sources of X-rays including black holes and neutron stars.
(Original title "Chinese scientists obtain the first batch of cosmic large field of view X-ray focused imaging sky map")