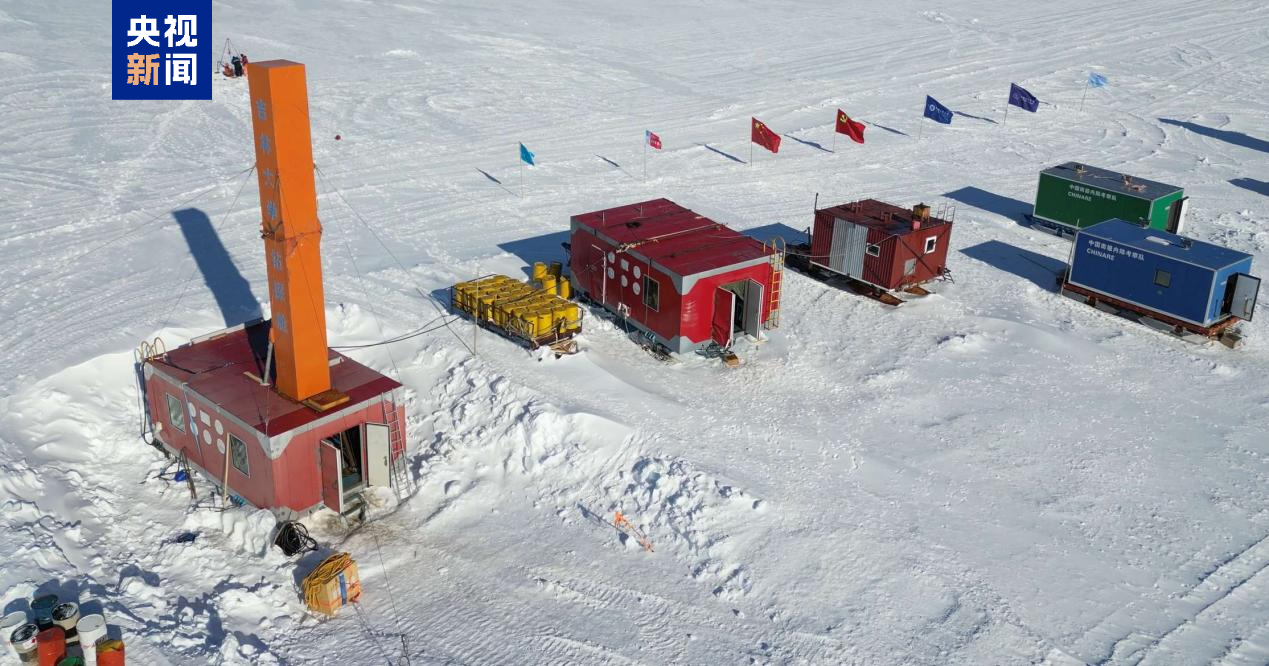
On February 28, the construction of the "Cold Spring Ecosystem Research Facility", a major national scientific and technological infrastructure, was fully launched in Guangzhou. The facility was applied for and constructed by the South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The project includes three parts: "undersea laboratory sub-general", "fidelity simulation sub-general" and "security support sub-general". This is also the world's first 2,000-meter-class bottom-seated deep-sea laboratory that can be manned for a long time.
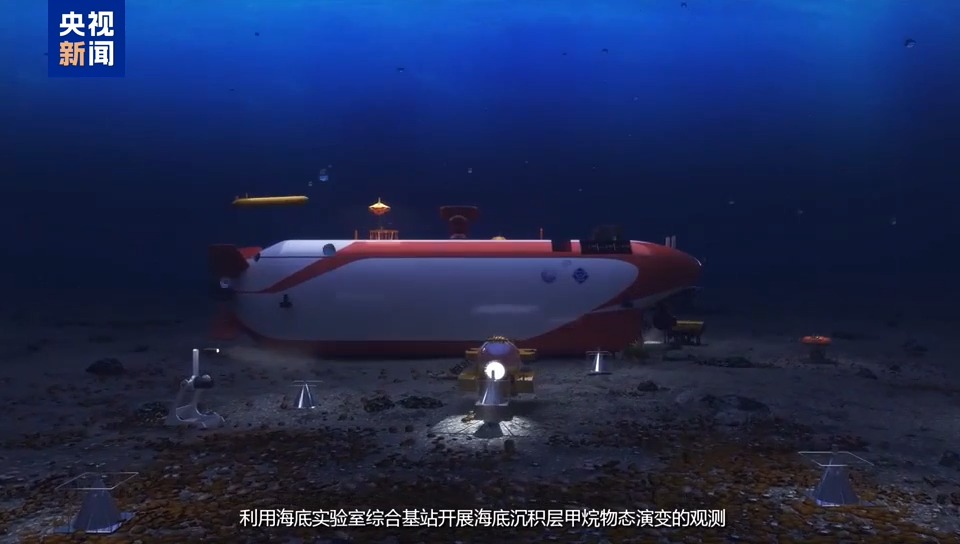
The cold spring device adopts the design concept of "sample site experiment + land simulation, sea-land coordination, time-space exchange". It is planned to build an internationally leading research device integrating a deep-sea manned resident submarine laboratory for cold spring ecosystems and land-based fidelity simulation facilities in five years to support the development of cold spring ecosystems, chemosynthetic biological succession, and methane physical evolution and its environmental effects. After the completion of the cold spring device, it will provide advanced platform support for cutting-edge basic research and high-tech research and development such as the exploration of the origin of life in extreme deep-sea environments and the green development of deep-sea resources such as methane hydrate, becoming a key step taken by my country in the field of deep-sea scientific research and serving the "ocean power" strategy and "dual carbon" goals.

"Cold springs" refer to the activities of gases such as methane, hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide under the seafloor, which overflow into the seawater driven by geological structures or pressure changes. The cold spring ecosystem refers to the use of chemical substances seeping from cold springs on the seafloor as energy for chemosynthesis by marine organisms, which develop into a unique ecosystem in the dark world of the seafloor. It has physical and chemical characteristics such as darkness, high pressure and low oxygen. It uses methane decomposed from combustible ice as a biogenic element and reproduces endlessly through chemosynthesis. It is known as the "deep sea oasis". The cold spring ecosystem carries the code of the deep carbon cycle of the earth and is a strategic location for studying the adaptation mechanism of life in extreme environments and exploring new biological resources. Conducting research on cold spring ecosystems is the best entry point for green development of deep-sea resources such as combustible ice and deep-sea scientific research. The cold spring device will provide a new perspective and technical means for the study of cold spring ecosystems and accelerate scientific research progress in related fields.

It is planned to build the world's first 2,000-meter-class deep-sea manned laboratory in five years.
The total construction plan for the cold spring device is to take five years to build the world's first 2,000-meter-class bottom-mounted deep-sea manned laboratory. This is also the world's first large-scale scientific facility for seabed cold spring systems. After completion, it will promote leapfrog development in marine science such as the development mechanism of cold springs, the evolution process of extreme life, and the ecological effects of combustible ice, and promote deep-sea scientific and technological progress.




Comments