
On the remote Antarctic Ross Sea Fort Island, at this moment, the builders of the new Ross Sea station are busy "building new houses." Ross Sea New Station, my country’s fifth scientific research station in Antarctica, completed the topping out of the main structure of the main building just a week ago. What does the new website look like? How is building a "new home" in Antarctica different from ordinary engineering construction?
Let’s first take a look, what kind of place is the Ross Sea? What method did the builders use to build the scientific research station in a short time?
How was the “Micro Science City” built in just two months?
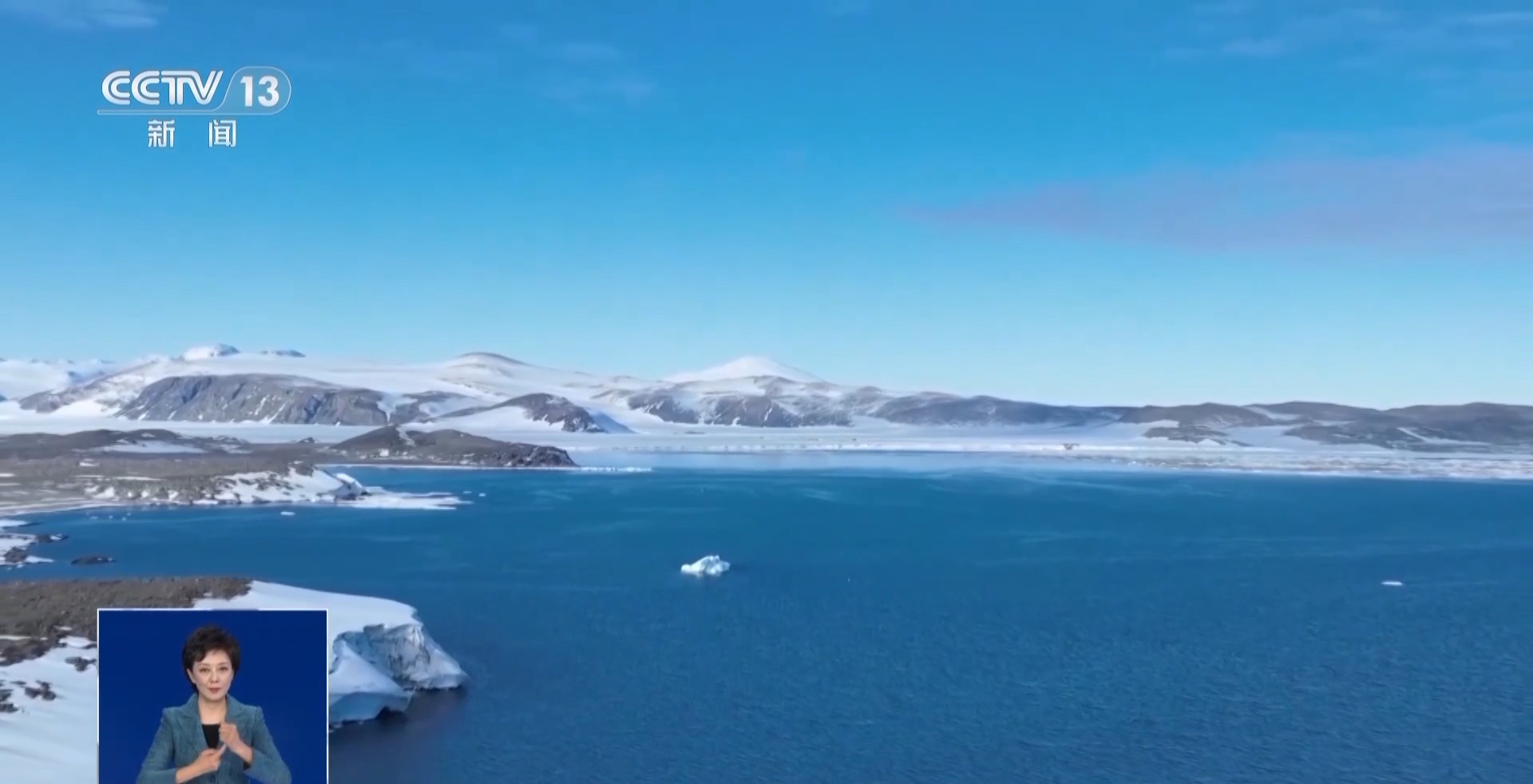

The Ross Sea has the largest ice shelf in Antarctica. It is the most active area of interaction between the Southern Ocean and the Antarctic ice sheet, and is also the area with the most critical impact on global climate. It also has the largest ice-free area in Antarctica, the McMurdo Dry Valleys, which is of great significance for the study of the lithosphere. Various countries in the world, including the United States, Italy, Germany, South Korea, etc., have built scientific research stations here. It is also a place where Antarctic powers gather. After our country establishes a scientific research station here, scientific research activities can be radiated to a surrounding area of 300 to 500 kilometers through helicopters, snowmobiles and other means of transportation, which will greatly enhance our country's scientific research capabilities and levels in West Antarctica.
Duan Meng, deputy chief architect of China Construction Technology Group China Architectural Design and Research Institute Co., Ltd. and chief designer of Rosshai New Station: It is not a simple building. It actually requires comprehensive consideration of its infrastructure, such as roads and docks. , energy, water treatment, including communications, these are all considered as infrastructure. In addition, the functions of the building itself, such as offices, scientific research, experiments, warehouse storage, personnel life, and personnel leisure, all these communication activities must be taken into consideration. In fact, as a small research station, it is actually a miniature science city.
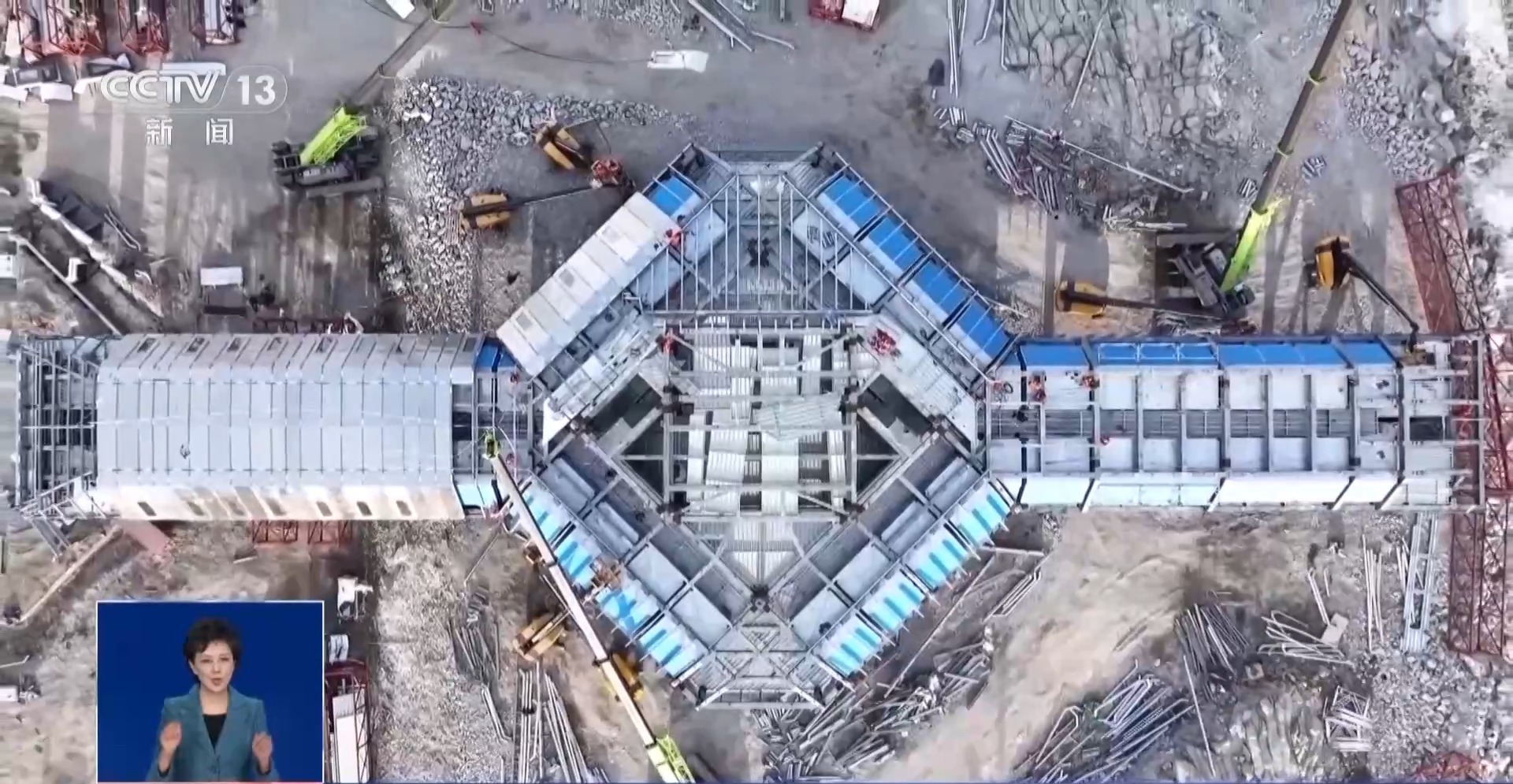

This "miniature science city" must be built within a short two-month time window. In addition to the construction of the main structure, 84 modules for internal use also need to be assembled, including 16 winter dormitory modules, 26 summer modules, as well as offices, scientific offices, etc.
Duan Meng, deputy chief architect of China Construction Technology Group China Architectural Design and Research Institute Co., Ltd. and chief designer of Rosshai New Station: These modules have actually accounted for 45% of the entire construction assembly rate. This module assembly and internal fine decoration can be completely completed in China. After arriving at the site, it can be quickly installed on the skeleton of our structure, and then further connected to our pipelines, you can move in with your bags. This is very fast.
How is steel structure production different in response to the harsh Antarctic climate?
First, the modules are produced separately, and then assembled together. This is how China's infrastructure geeks quickly built the new Ross Sea station. The Antarctic climate environment is harsh, and the location of the new Ross Sea station is particularly windy. The main building of the new station is mainly made of steel structure. How to ensure its sturdiness?
In the area where the new Antarctic Ross Sea station is located, the temperature is below minus 40°C. When the temperature is lower than minus 35°C, the steel will appear "cold brittleness", its toughness will be reduced, and it will easily break. This company located in Xuzhou, Jiangsu Province searched many places before finding this special material that can withstand extreme cold.

The construction workload of new stations is heavy and the construction window period is short. In order to further reduce on-site installation errors and improve construction efficiency, the project adopted large modular construction technology, and the steel structure components used were all extended versions of conventional projects.

Chen Rui, chief engineer of the General Engineering Office of a steel structure company in Jiangsu: The longest column (in the Antarctic project) is 16.5 meters, which may be twice as long as this column. The conventional standard is generally within 12 meters. The difficulty of transportation has also increased, and the requirements for our processing are also higher.
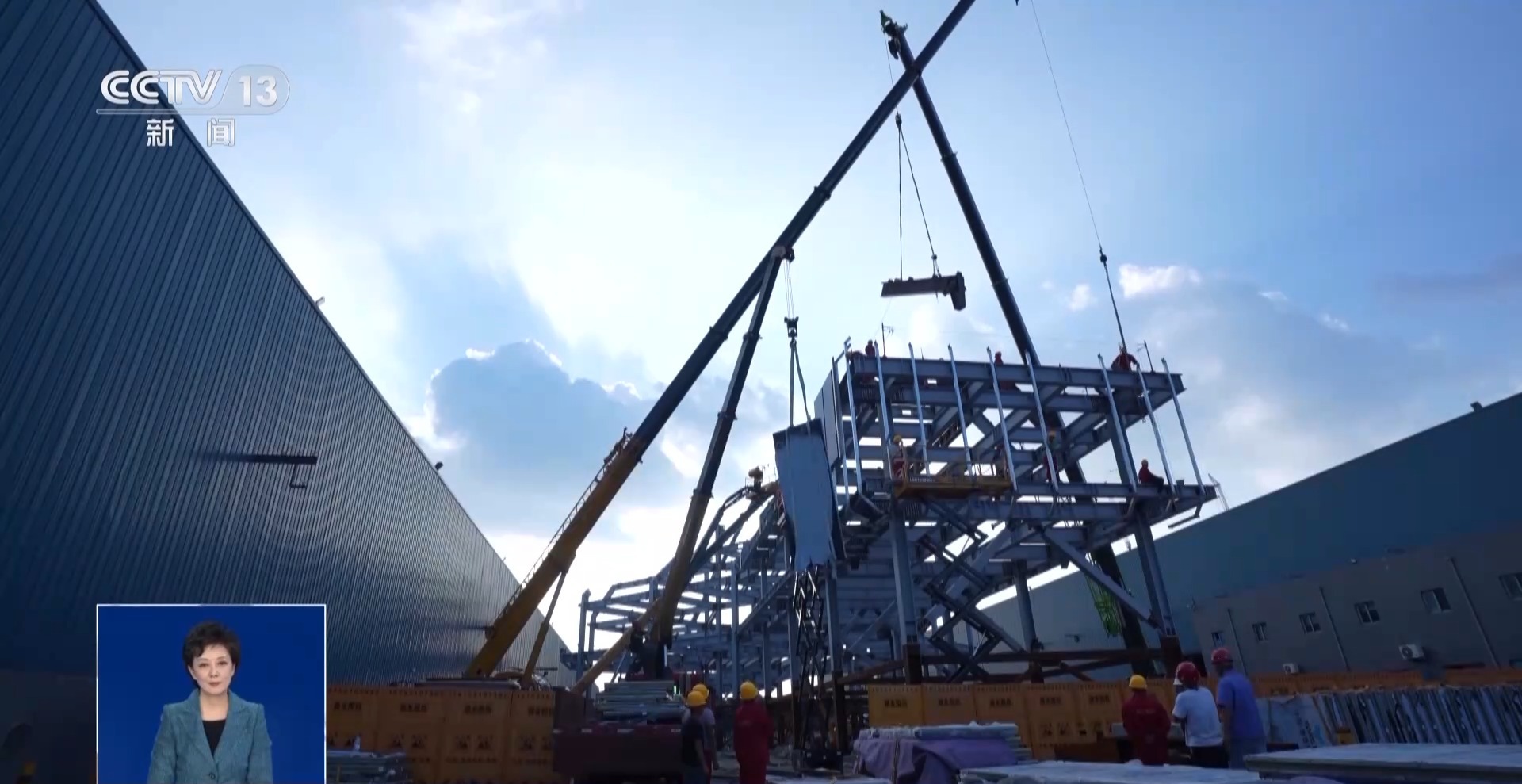

According to reports, this fully assembled steel structure has a total of 4,134 components, 49,989 parts, a total of 71,572 sets of bolts, and a total of 220,000 holes.

In order to ensure a successful one-time installation at the construction site, pre-assembly was carried out in Xuzhou before shipment, including all links from assembly to packaging and transportation, ensuring that "building a house like building blocks" can also be achieved in Antarctica.
What is the special design of more than 70,000 sets of "Antarctic bolts"?
Because Antarctica does not have on-site welding conditions, the steel structure of the new Ross Sea station is connected by more than 70,000 sets of high-strength bolts, all of which are made in China. To withstand the extreme climate of Antarctica, what are the special designs of these "Antarctic bolts"? How is it made?
Yang Zhaojun, general manager of a fastener company in Anhui Province: On the surface, it looks like steel bars, but it is actually a kind of special steel, a special weathering steel. Compared with ordinary steel, this kind of steel has more than a dozen special elements such as niobium added to it to solve some of the properties of steel in various aspects such as ultra-low temperature impact.
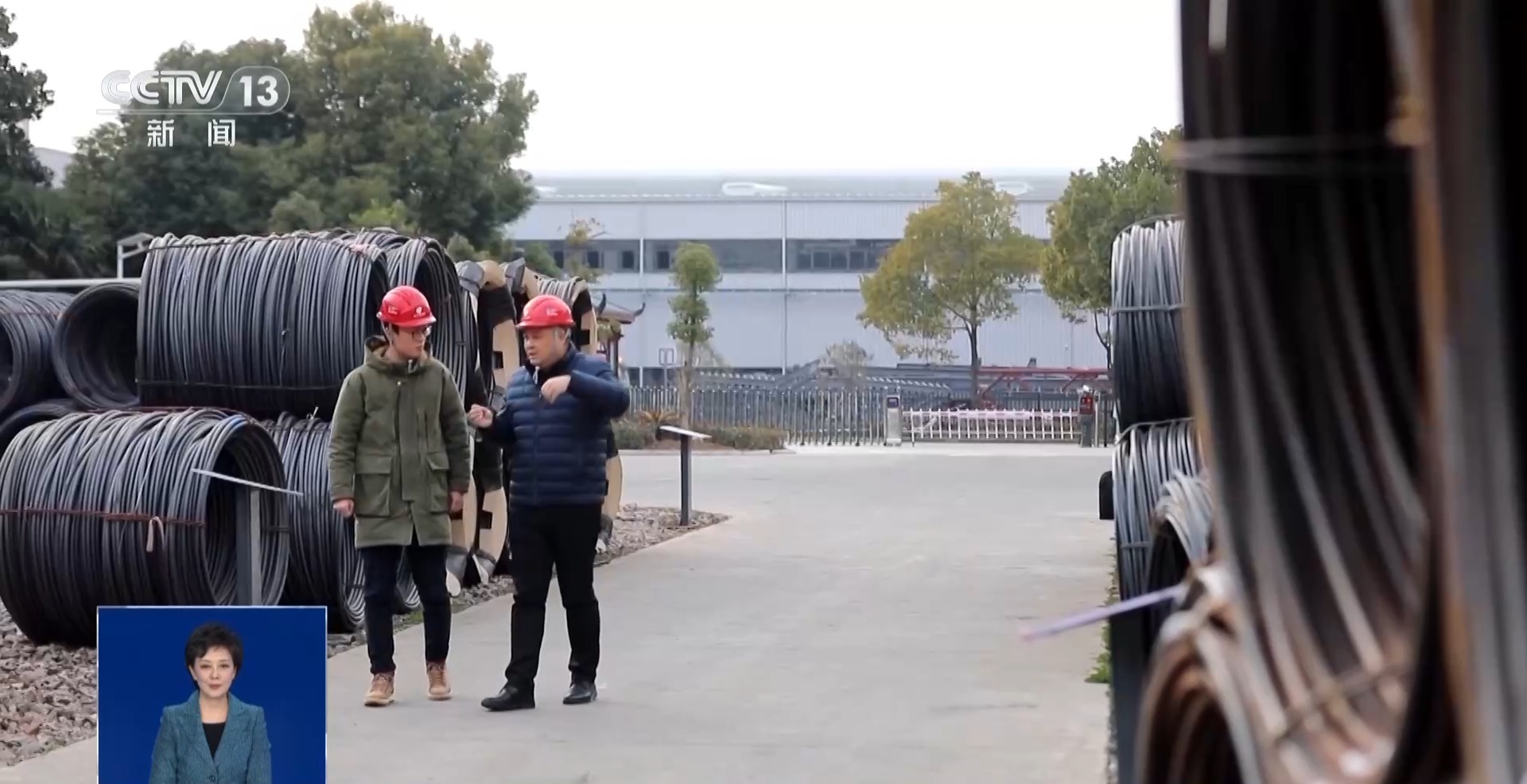

In the company's open-air storage yard, there are all such special steels, which are 3,000 yuan more expensive per ton than ordinary steel. Since they are so valuable, why not pile them in a warehouse?

Yang Zhaojun, general manager of a fastener company in Anhui: It facilitates subsequent deep processing. Its material toughness and elasticity are different, so during subsequent deep processing, it will affect the damage and accuracy of the mold.

Yang Zhaojun told reporters that just like soybeans that need to be exposed to the sun to make soy sauce, these special steels also need to be stored in the open-air stockyard for two months before they can be processed in the next step.

This production workshop does not look "high-end", but there are innovative designs and "indigenous inventions" made by the R&D team everywhere.
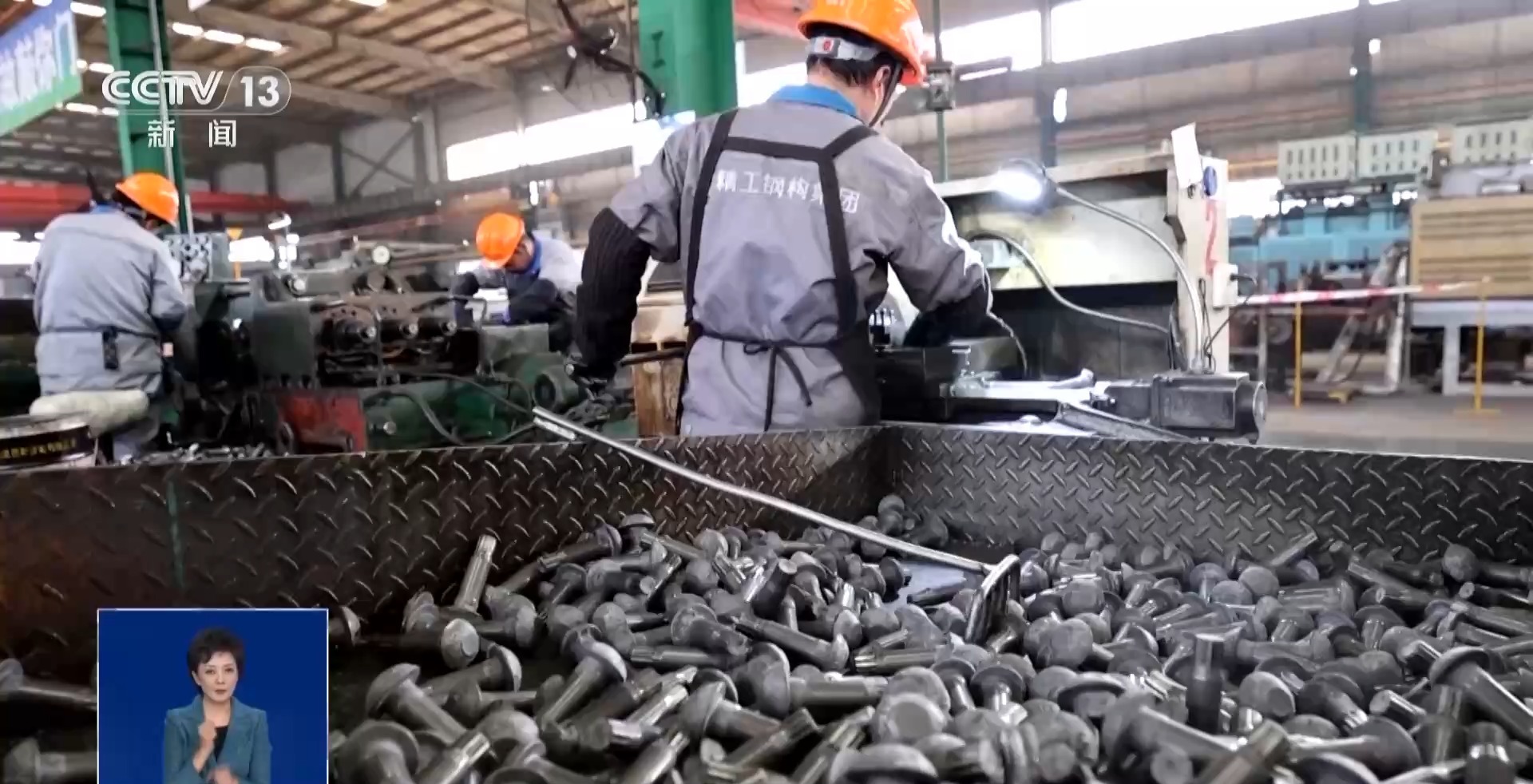

After the round steel is processed by the front end of the material and becomes shiny, it can be processed and formed. The mainstream method in the industry is either cold press forming, but this will cause cracks inside the steel. Either it is heated and reprocessed, which is called "red beating", but the bolts made in this way cannot adapt to the extreme climate of Antarctica.

Yang Zhaojun, general manager of a fastener company in Anhui: Our molding process is called "warm beating". We heat it at more than 600°C to 700°C to make it. This solves the problem of cracks in "cold beating" and there are no cracks inside.

A "warm-beating" formed bolt also undergoes heat treatment and chemical treatment, and finally becomes a "weather-resistant and delayed-fracture-resistant high-strength bolt" that is completely black and can be used in Antarctica. But that's not all. In this laboratory, the bolts still need to be tested for reliability. From every 3,000 groups of bolts, 8 groups are randomly selected and tested for impact performance in a simulated extreme cold environment.

Zeng Hui, deputy chief engineer of a fastener company in Anhui: Ordinary steel structure bolts may break at -60°C with an impact force of six or seven joules, but the screws we supply to the Ross Sea in Antarctica, At -60℃, it can reach the range of 67 to 70 multi-joule impact force.
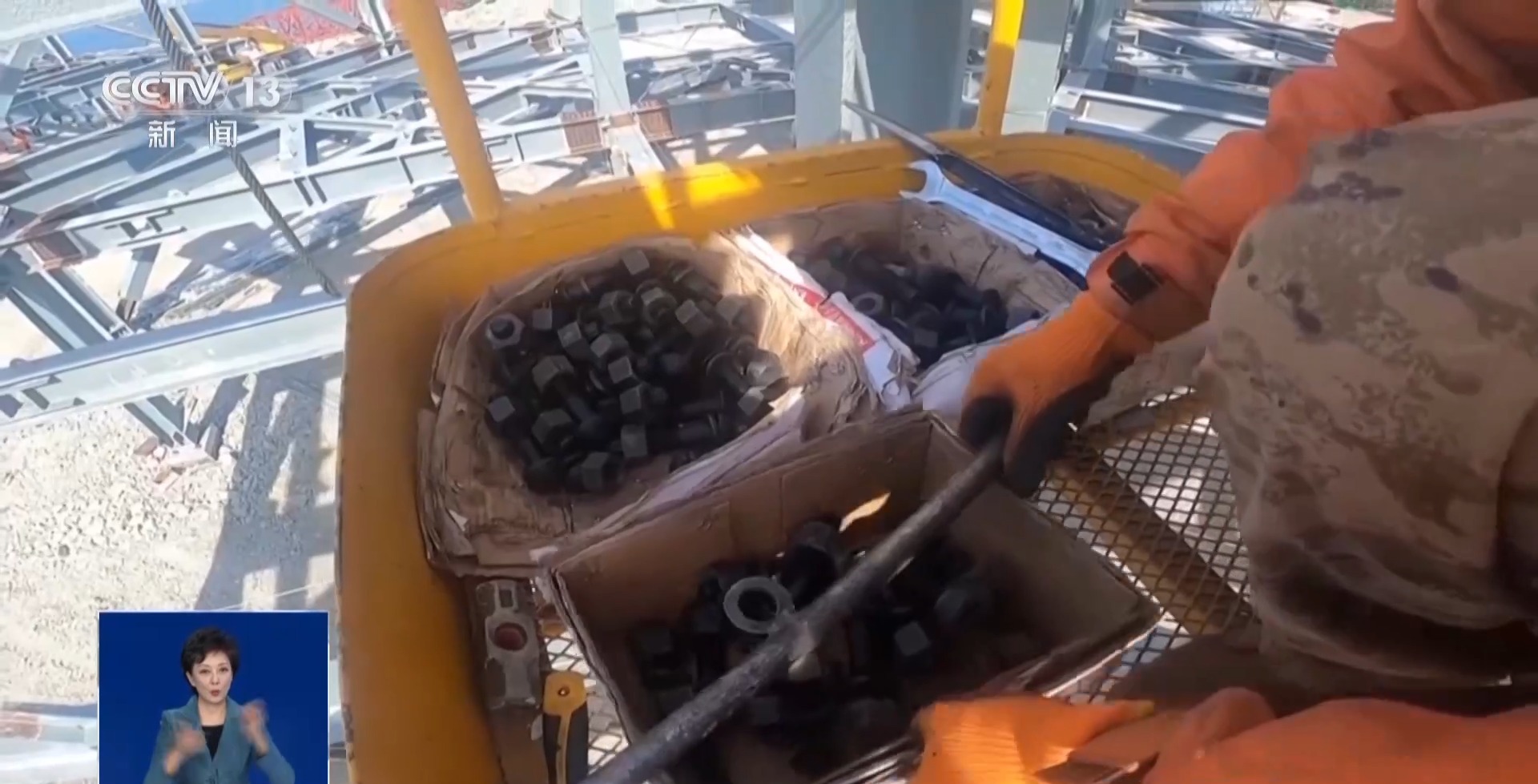

An inconspicuous bolt, after being polished by the R&D team and workers for excellence, finally crossed the Pacific and landed in Antarctica, becoming the "Selected National Team".
What are the challenges in building a helipad on Enxburg Island?
Whether transporting cargo or people in Antarctica, helicopters are indispensable. Therefore, the apron is also a necessary infrastructure for every scientific research station. my country's Ross Sea New Station will also build an apron covering an area of 1,020 square meters. The more than 400 special building materials used to pave the apron were all developed and manufactured in my country. What challenges are faced in the construction of apron?
In the factory of China Construction Technology (Huzhou) Co., Ltd. located in Jiuguan Town, Nanxun District, Huzhou City, the intelligent production line is producing prestressed standardized prefabricated pavement panels. This prefabricated pavement panel is manufactured according to specific requirements. The overall stiffness and resistance of the components are It has better cracking ability and overall durability, and can adapt to the harsh climate conditions of Antarctica.
He Liang, leader of the Antarctic apron research team of China Construction Technology Group East China Co., Ltd.: In the Antarctic environment with low oxygen content, low temperature, and high wind speed, if the traditional construction model is adopted, the construction period and product quality cannot be guaranteed. But we start from the source, using high-strength concrete that can be repeatedly frozen and thawed more than 200 times, and apply prestressed technology to the production and manufacturing of our product.
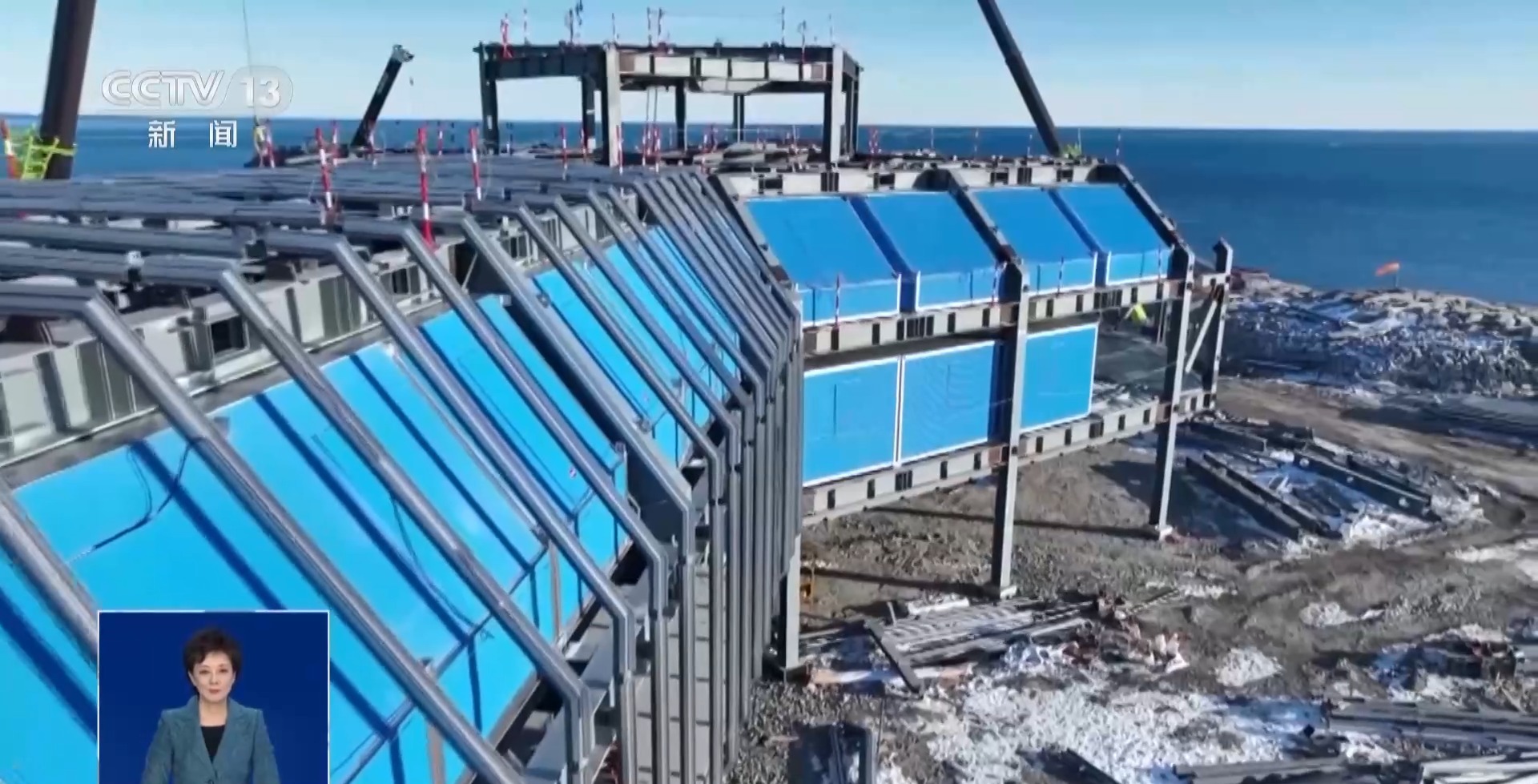

It is difficult to "build" in Antarctica, and there are many "stumbling blocks" that need to be faced, among which the harsh natural environment and complex geological conditions are the key to avoidance. Compared with the traditional construction model, the prefabricated apron has the characteristics of fast construction, less turnover materials and high degree of mechanization, which can better adapt to the construction requirements of the Ross Sea new station.
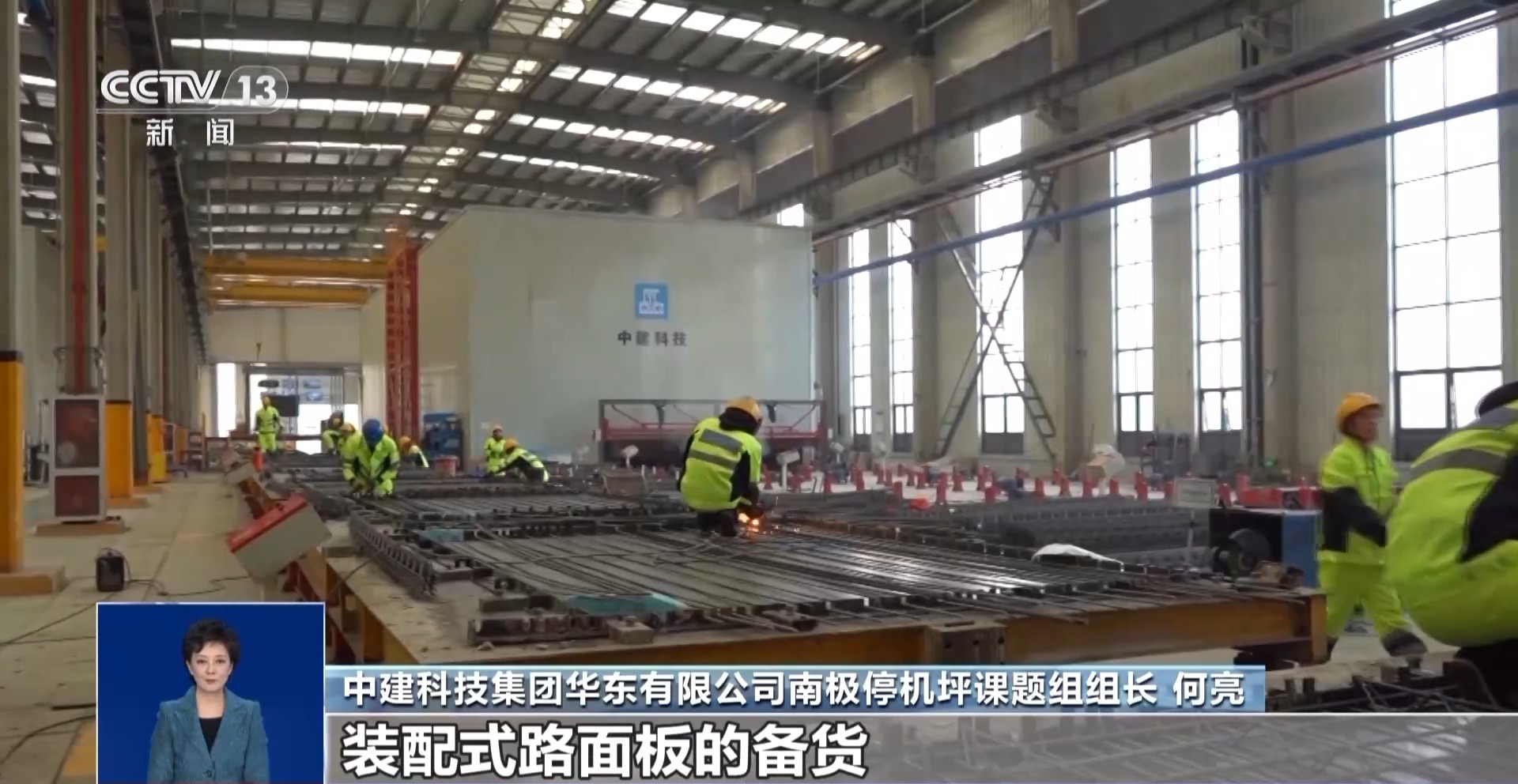

He Liang, leader of the Antarctic apron research team of China Construction Technology Group East China Co., Ltd.: It took only 10 days of production to complete the stocking of more than 400 prestressed standardized prefabricated pavement panels.
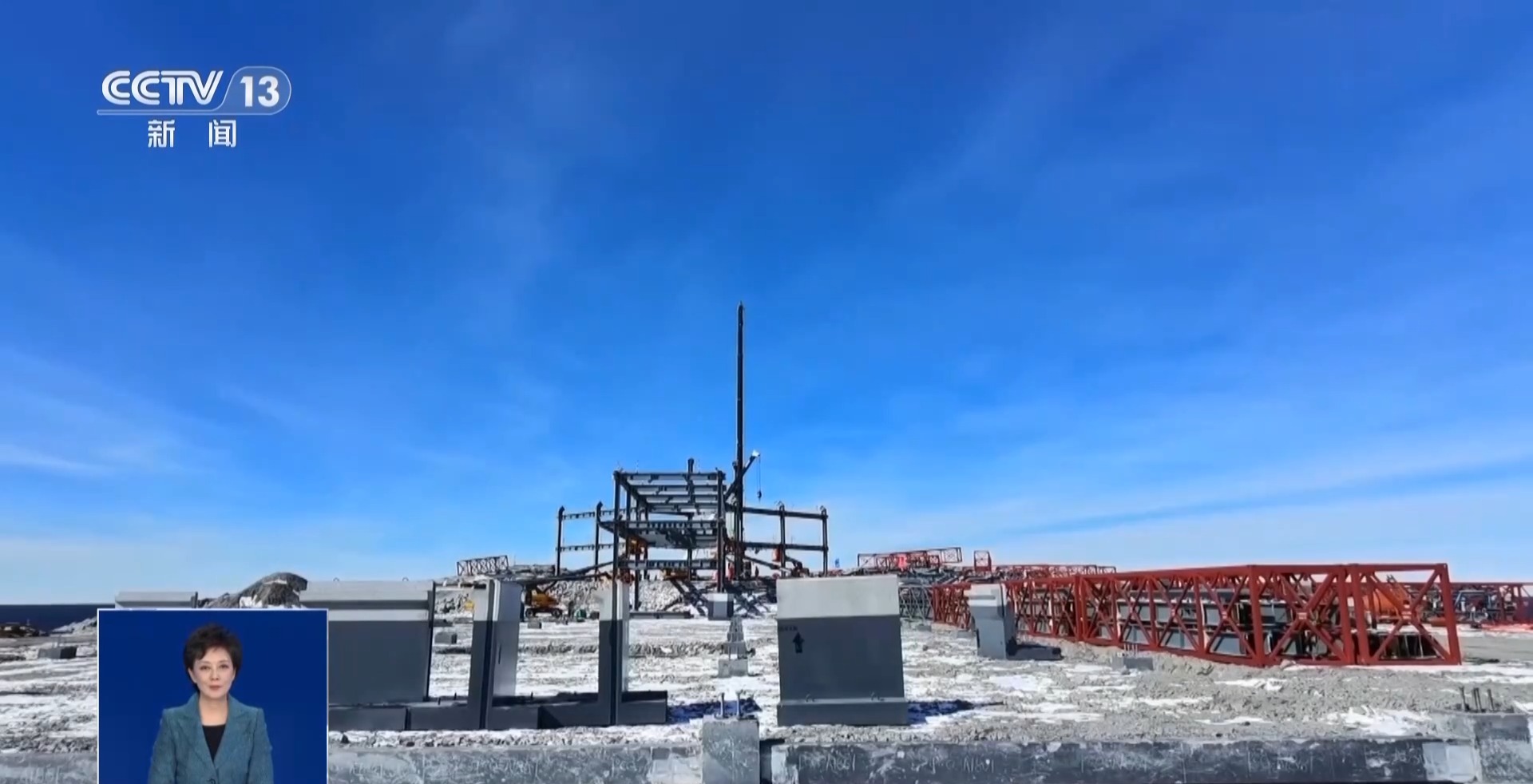

After more than two months of traveling across the ocean, these more than 400 road panels have been successfully shipped to Antarctica through container assembly. After the apron is assembled, ships entering the Antarctic continent can bring relevant supplies and scientific research equipment to the island, and depart from the apron to various scientific research sites.
(CCTV reporters Liang Lijuan, Chen Bo, Li Jie, Song Yunyan and Yang Ying)


