
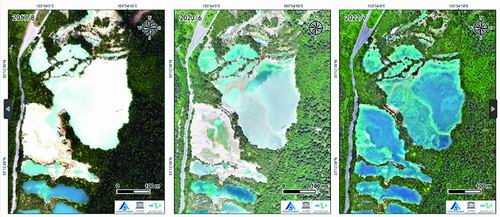
UAV remote sensing images of the sparkling waters in 2017, 2020 and 2022. Photo courtesy of Kongtianyuan
Recently, the Aerospace Information Innovation Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (hereinafter referred to as the Aerospace Institute) and the UNESCO International Natural and Cultural Heritage Space Technology Center (HIST) released the remote sensing monitoring results of the dynamic changes of the Jiuzhaigou World Heritage after the earthquake. The results show that the vegetation in the Jiuzhaigou area has been gradually restored, and the sparkling sea that has attracted much attention has returned to its former beauty.
On August 8, 2017, a 7.0-magnitude earthquake occurred in Jiuzhaigou, and the quality of the ecological environment in the heritage site was seriously damaged. In order to promote the recovery and development of Jiuzhaigou, Fu Bihong, a researcher at the Aerospace Academy, led the Jiuzhaigou "sky-space-ground" monitoring project. During the three-year research, the project developed the Jiuzhaigou Protection and Restoration Spatial Information Monitoring System, built an international scientific and technological consultation and training platform for World Heritage protection and management, and provided important scientific data and technical support for the protection and management of Jiuzhaigou.
Analysis of remote sensing images shows that the vegetation coverage of Jiuzhaigou in 2017 (before the earthquake) accounted for 82.11% of the total area of the whole region, and the proportion of vegetation coverage dropped to 79.91% after the earthquake. With the development of post-earthquake restoration and reconstruction, the proportion of vegetation coverage will rise to 81.07% and 80.91% in 2020 and 2022, respectively, and the vegetation coverage will be close to the pre-earthquake level.
The research team divided the overall vegetation coverage of Jiuzhaigou into five levels: high, high, medium, low and low. Among them, the area of low and low vegetation coverage has been significantly reduced, transformed into medium and high vegetation coverage, and the stability of vegetation coverage has increased, indicating that the post-earthquake ecological restoration of Jiuzhaigou has played a positive role in recent years. Among them, the restoration of vegetation is concentrated in the Rize Valley and Zechawa Valley of the Jiuzhaigou Natural Heritage Site, and the vegetation recovery on the southwestern edge of the Panda Sea-Wuhua Lake line is the best.
As an important heritage point of Jiuzhaigou Heritage Site, Huohuahai is the focus of monitoring by the research team. Remote sensing images show that after the post-disaster restoration and reconstruction, the calcified dam in the Huahuahai collapse area has been repaired, and its water body has basically recovered. It has reopened to the public in October 2020. Fu Bihong said that from the images obtained by drones in July 2022, it can be seen that the repaired Huohuahai Dam is stable, the upstream water is sufficient, the water is clear, the surrounding vegetation has basically recovered, and it has gradually returned to its former beauty.
In order to quantitatively study the spatial distribution and changes of landslide susceptibility after the earthquake, the research team counted the proportion of landslide-prone areas of each level in 2017, 2017-2019 and 2019-2020. The post-earthquake landslide susceptibility results from 2017 to 2019 show that compared with 2017, the high and extremely high susceptibility areas dropped rapidly to 11.00%; the proportion of extremely low susceptibility areas increased rapidly, from 13.56% to 51.87%. The results of post-earthquake landslide susceptibility in 2019-2020 show that compared with 2017-2019, the high and extremely high susceptibility areas continued to decrease, and their total proportion dropped from 11.00% to 8.71%; the extremely low susceptibility areas continued to expand, Its proportion rose from 51.87% to 55.57%.
The data show that after the natural recovery after the disaster and supplemented by artificial restoration, the risk of geological disasters in the Jiuzhaigou Heritage Site has been greatly reduced.
(Original title "The sea of sparks has been restored! Release of remote sensing monitoring results after the Jiuzhaigou earthquake")