
The reporter learned from the Institute of Microsatellite Innovation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences that the second batch of scientific and technological achievements of my country's "Innovation X" series of first satellites, the space new technology experimental satellites, have been released recently. These achievements mainly include the acquisition of my country's first image of the solar transition zone, the detection of the brightest gamma-ray burst so far, and the first global magnetic field survey map.
The 46.5nm extreme ultraviolet imager obtained my country's first image of the solar transition zone
The 46.5nm Extreme Ultraviolet Solar Imager (SUTRI) is the world's first 46.5nm solar imager based on multilayer film narrow-band filter technology, which is used to detect the solar transition zone of about 500,000 degrees (the layer between the solar chromosphere and the corona) ), jointly developed by the National Astronomical Observatory, Peking University, Tongji University, Xi'an Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics and Microsatellite Innovation Research Institute. Since the load was turned on on August 30, 2022, more than 1.6TB of detection data has been obtained, and my country's first detection of the solar transition zone has been successfully realized. This is also the first time that humans have taken a complete image of the sun in the 46.5nm band in the past half a century. The images taken by SUTRI clearly show structures such as the network organization of the transition region, the coronal loop system in the active region, prominences and dark stripes, and coronal holes (Fig. 2). The structure of the transition to the corona, as expected. SUTRI has detected multiple flares, jets, prominence eruptions and coronal mass ejection events (as shown in Figure 3), indicating that its data are suitable for studying various types of solar activity phenomena. In addition, SUTRI also found that there are generally material flows of about 500,000 degrees in the active region toward the surface of the sun, and these flows play an important role in the material circulation process of the solar atmosphere. At present, all functions of SUTRI are normal. After the on-orbit test and calibration are completed, the scientific data observed by SUTRI will be open to domestic and foreign heliophysics and space weather colleagues.

Figure 1 "Innovation X" launch star - new space technology test satellite (SATech-01)
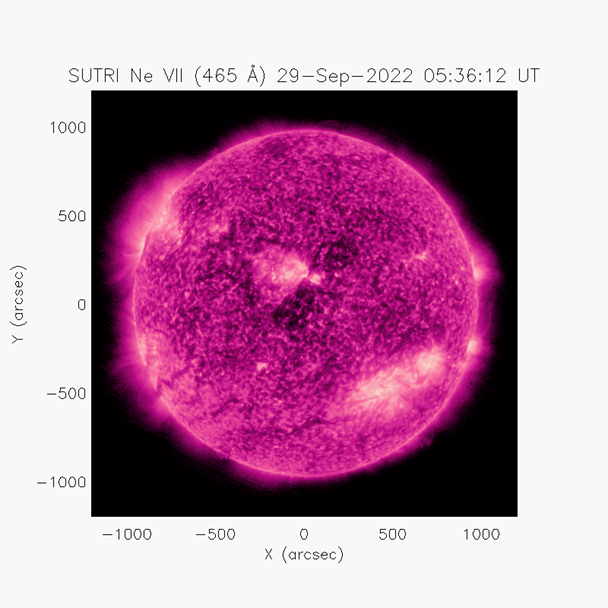
Figure 2 Solar activity map observed by SUTRI on September 29, 2022 (picture provided by the SUTRI science team)
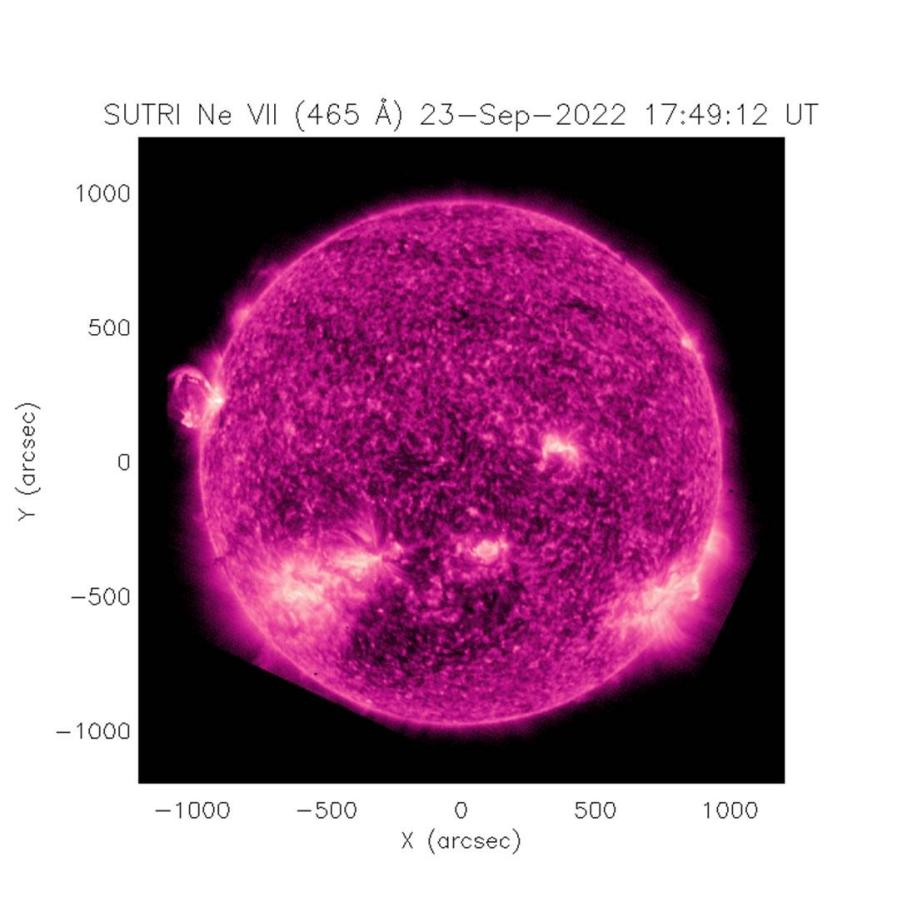
Figure 3 A solar outburst event observed by SUTRI on September 23, 2022 (picture provided by the SUTRI science team)
High Energy Burst Explorer (HEBS) captures brightest gamma-ray burst to date
The High Energy Burst Explorer (HEBS) developed by the Institute of High Energy Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences detected the brightest gamma rays so far at the same time as my country's Huiyan Satellite and the High Altitude Cosmic Ray Observatory at 21:17 on October 9, 2022, Beijing time. storm (numbered GRB 221009A). According to the precise measurement results of HEBS, this gamma-ray burst is more than 10 times brighter than the brightest gamma-ray burst ever observed by humans. Due to the extremely high brightness of the gamma-ray burst, most of the detection equipment in the world suffered from serious instrument effects such as data saturation loss and pulse accumulation, making it difficult to obtain accurate measurement results. With innovative detector design and novel high-latitude observation mode setting, HEBS has withstood the test of high count rate, obtained light curve with high time resolution, and a wide range of 10 keV to 5 MeV. energy spectrum. The extremely precious and precise measurement results of HEBS are of great significance for revealing the origin and radiation mechanism of gamma-ray bursts.
The EP Pathfinder Lobster Eye X-ray Imager (LEIA) developed by the National Astronomical Observatory and the Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics also successfully observed this gamma-ray burst on October 12, and detected the gamma-ray burst X-ray afterglow . This is also the first time in the world that a gamma-ray burst has been detected with a lobster-eye X-ray telescope.
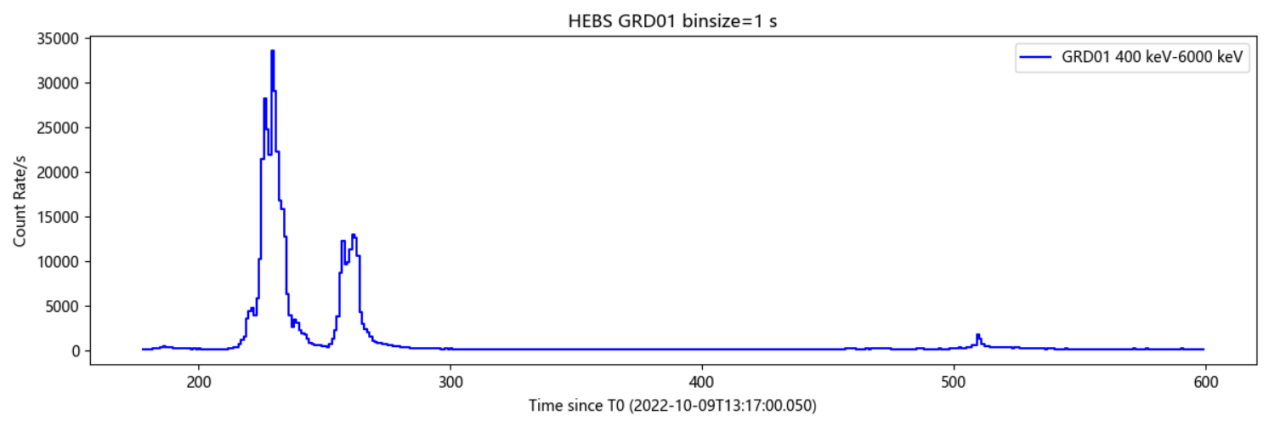
Figure 4 The High Energy Burst Explorer (HEBS) discovered and accurately measured the brightest gamma-ray burst so far, breaking multiple records.
The domestic quantum magnetometer is applied in space for the first time and obtains the global magnetic field map
The domestic quantum magnetometer (CPT) and extension arm jointly developed by the National Space Science Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Shenyang Institute of Automation can realize global geomagnetic vector and scalar high-precision measurement. On November 7, 2022, the multi-level sleeve-type non-magnetic extension arm was successfully launched, and each sensor probe was extended to a distance of about 4.35 meters. The CPT atomic/quantum magnetometer probe, AMR magnetoresistive magnetometer probe, and The NST star sensor has obtained effective detection data, and the integrated synchronous detection technology of magnetic field vector and attitude has been verified for the first time in orbit, and the peak-to-peak noise of magnetic measurement is <0.1nT, realizing the first space verification and application of domestic quantum magnetometer.

Figure 5 CPT magnetic measurement system "multi-level sleeve type non-magnetic extension arm" ground test (picture provided by Shen Zi Institute, space center and satellite team)
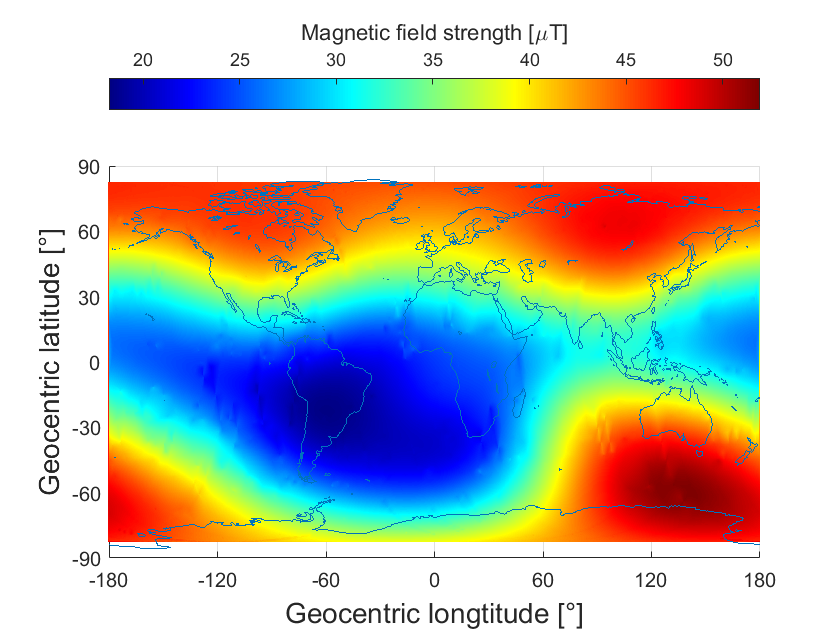
Figure 6 The first global magnetic field survey map of the quantum magnetometer (picture provided by the Key Laboratory of Solar Activity and Space Weather of the Space Center)
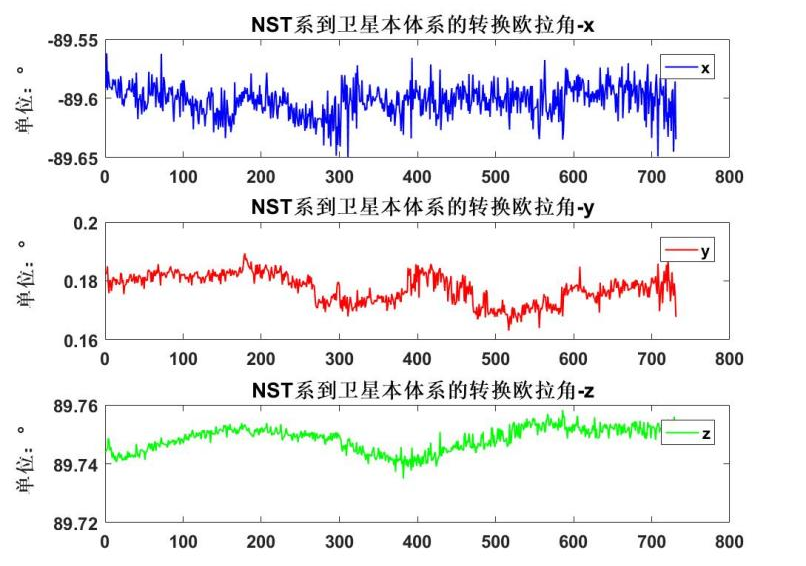
Figure 7 The attitude data of the NST star sensor relative to the satellite body (the picture is provided by the Space Center and the NST Star Mining Team of the New Roentgen of the Chinese Academy of Sciences)
Abundant achievements in new technologies for space payloads and platforms
The multi-functional integrated camera developed by the Space New Technology Department of the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, for the first time adopts a new system based on a common-aperture multi-exit pupil optical system, and realizes the integration of visible light, long-wave infrared, and color low light in orbit space optical remote sensing observations. The camera was turned on on September 24, 2022, and successfully obtained the first 170km×42km wide ground remote sensing image (as shown in Figure 8). my country's future development of highly integrated space optical remote sensing payloads provides a technical reserve.

Figure 8. Wide-scale remote sensing imaging of the ground with a multi-functional integrated camera (picture provided by Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics)
The heterogeneous multi-core intelligent processing unit jointly developed by the Institute of Semiconductors, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of Microsatellite Innovation, and Institute of Aerospace Information Technology, School of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Zhejiang University has also achieved the first batch of results. The low-power edge computing intelligent remote sensing vision chip of the Institute of Semiconductors has realized the high-speed intelligent target detection of remote sensing images; the general intelligent system of the Institute of Automation has verified the heterogeneous multi-processor modularization and flexible hardware architecture based on high-speed switching networks ;The domestic AI system of Zhejiang University is loaded with cell segmentation algorithm and aircraft recognition algorithm, the data results are consistent with the data of the ground twin system, and the computing power reaches 22Tops under the condition of power consumption of 10 watts, which verifies the on-orbit intelligent image processing capability of domestic AI devices .

Figure 9 Schematic diagram of edge computing remote sensing vision chip detecting remote sensing targets (picture provided by Semiconductor Institute of Chinese Academy of Sciences)
The expandable and retractable radiator of the Microsatellite Innovation Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has successfully achieved its first application in orbit. The actuator of the radiator has successfully completed more than 60 times of deployment and retraction. The dynamic test results of five consecutive orbits (as shown in Figure 10) show that the loop heat pipe -The retractable radiator integrated system has good start-up performance during the load working period, and the continuous deployment and retraction of the radiator can realize a wide range of on-orbit regulation of the cooling capacity.
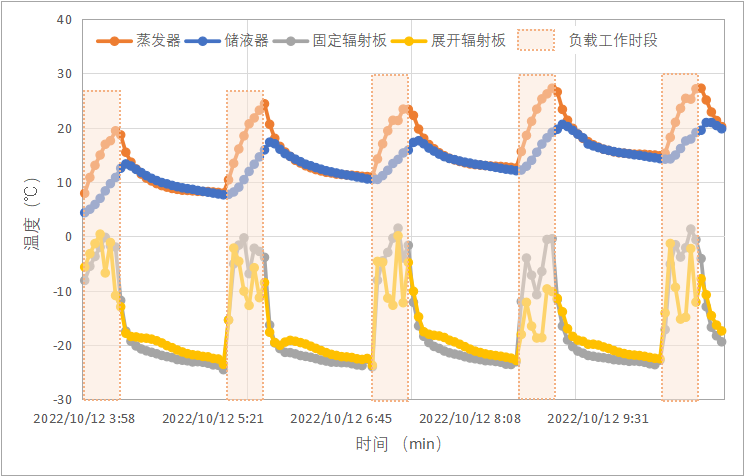
Figure 10 Continuous five-track intelligent thermal control test results of the loop heat pipe-expandable radiator integrated system
The payload of the radiation effect test platform for space components developed by the National Space Science Center is running well, and the components on board are working normally during the test period.
"The emergence of scientific and technological achievements embodies our positioning of this satellite as 'innovation X, innovation without limit', creating a precedent for new technology crowdfunding models." "Lijian-1" Deputy Chief Engineer and Satellite System Chief Teacher Zhang Yonghe said, "These new payloads and new technology products are independently invested by all participants, and many of them are innovations from 0 to 1. The rapid integration and flight verification of innovative technologies through test satellites can speed up the transformation of core key technologies from 0 to 1. Transformation of results from basic research to on-orbit applications."
At 12:12 on July 27, 2022, my country's largest solid launch vehicle "Lijian-1" (ZK-1A), independently developed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, was successfully launched at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center. In this way, six satellites, including the first star of the "Innovation X" series - space new technology test satellite, will be sent into the predetermined orbit. On September 5, 2022, the Space New Technology Experiment Satellite (SATech-01) released the first batch of scientific results, including the world's first wide-field X-ray focused imaging sky map of the Lobster Eye X-ray Imager (LEIA), gamma The first gamma-ray burst of ray burst load (HEBS), etc.
As the first star of my country's "Innovation X" series, in the future, several new propulsion systems and other loads carried by space new technology test satellites will also carry out on-orbit tests, and the four scientific loads on the satellites have also entered routine observation. More scientific and technological achievements will be obtained in succession.


