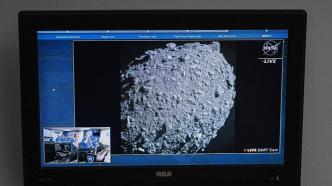
The impact was humanity's first planetary defense experiment to test our ability to redirect the paths of potentially threatening asteroids.
Space telescopes will watch to see how much the impact changed the asteroid's motion, and it could take months to get a full picture of the results. If all goes according to plan, the impact will shorten the rotation period of the target asteroid by a few minutes, albeit not much, but could allow future asteroids to collide around Earth.
"We're entering a new era of humanity in which we may have the ability to protect ourselves from dangerous asteroid impacts," said Lori Glaze, director of NASA's Planetary Science Division. this ability.”
At 19:14 on September 26th, Eastern Time, NASA's "Double Asteroid Redirection Test" (DART) spacecraft successfully hit the asteroid "Dimorphos", hoping to deviate it from its original orbit , completed the test mission to test whether the "killer asteroid" can be deviated from the earth.
The impact was humanity's first planetary defense experiment to test our ability to redirect the paths of potentially threatening asteroids.
NASA is not the only actor. Wu Yanhua, deputy director of the China National Space Administration, previously stated in an exclusive interview with CCTV that my country is setting up a near-Earth asteroid defense system and may conduct an asteroid impact defense test in 2025 or 2026. .
"Autopilot", "Smashing the Stone with the Pebble"
SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket took on the mission of launching DART, the word DART means dart in English. And its impact on the asteroid is not as heroic as it appears in science fiction movies, but more like "hitting a stone with an egg". The spacecraft sent to impact is a cube of sensors, antennas, ion thrusters, and two 8.5-meter-long solar cell arrays that, while weighing 550 kilograms, are tiny compared to the planets.
Hits are difficult. After the last adjustment, the aiming accuracy of the DART was only two kilometers. Until an hour before the impact, the equipment onboard DART could not observe the 160-meter-diameter "Dimophos". In some of the early images sent back to Earth, even Didymos, its larger companion, the 780-meter-diameter Didymos, looked like a speck in a black ocean. But as the spacecraft was moving at 14,000 miles per hour, the details of "Dimovers" quickly emerged. Audiences on Earth saw the rough surface of Didymus as the spacecraft "autopilot" approached "Dedymos." The rock fills the screen before it turns red, indicating that Dart has reached its final destination.
When the images came back, the staff in the mission operations room were full of curiosity. "This asteroid came into view for the first time, and we didn't really know what to expect. We didn't know the shape of the asteroid, but we knew where we were going to hit," said DART mission systems engineer Elena Adams. So it felt like we were all holding our breath. In that second, none of us fainted."
Now, space telescopes around the world and several operating in space, including the James Webb Space Telescope and the Hubble Space Telescope, are turning their attention to the impact site to see how much the impact changed," Dimo said. Firth's campaign, it may take months to get a full picture of the results, but some images and data may come back in the days and weeks ahead.
Before impact, DART's spacecraft released a smaller satellite, the Italian-made LICIACube. The tiny spacecraft followed DART and captured the aftermath of the moment of impact, pictures that will be sent back to researchers on Earth.
Then in 2024, the European Space Agency will send another spacecraft to investigate Dimovers and get a close-up look at the asteroid and remnants of the spacecraft itself.
Meanwhile, the final images from the spacecraft provided researchers with a wealth of detail. Carolyn Ernst, a scientist working on the DART imaging system DRACO, described the shapes of the two asteroids, as well as the rocks, smooth sections and craters on the briefly visible Didymos, in a post-impact news conference.
If all goes as the researchers expected, the impact would have shortened the period in which Deimos and Didymus orbit each other by a few minutes. A few minutes, while not much, could allow future asteroids to bypass Earth.
Eliminate human fears from time immemorial
Scientists have carefully considered the choice of "Demovers" for the impact. First, they do not pose any threat to Earth, regardless of the outcome of the impact. Second, from the perspective of Earth, the two asteroids can block each other, and astronomers can use ground-based telescopes to measure the changes in light produced as they orbit each other to calculate their orbital periods. Finally, Dimovers is small enough that the impact can produce observable periodic changes.
In addition, the impact time of DART is also carefully selected. At the time of impact, the distance between Earth and the target asteroid was at a minimum of 11 million kilometers. Closer distances allow astronomers to improve the quality of their observations.
Neither Deimos nor Didymus posed any danger to Earth before impact. Currently, there are no known asteroids that pose a significant and immediate threat to Earth, but there is no guarantee that asteroids will not crash into our planet in the future.
In the movie, human beings have expressed their worries about the earth being crashed countless times, and this is not groundless. According to "Global Science", in 1994, a comet named Shoemaker-Levy smashed into Jupiter. The comet split into 21 pieces before the impact, the largest of which had an impact force as high as 6×10¹² A ton of TNT, equivalent to 600 times the human nuclear stockpile, scars the surface of Jupiter larger than the entire Earth. Even more frightening is that in 2013, an asteroid with a diameter of 20 meters exploded nearly a thousand meters above Chelyabinsk, Russia, with a power of about 450,000 tons of TNT, equivalent to a W88 nuclear warhead, causing 1,600 injuries. At present, mankind has discovered 29,000 near-Earth objects, of which 2,270 are potentially threatening objects.
Not to mention, about 65 million years ago, dinosaurs went extinct because of meteorites. And today humans have far more advanced technology than dinosaurs.
The impact experiment is not just to protect the earth. When people's understanding of space is incomplete, the test of asteroid impact is very valuable experimental data, and it can also help us better understand space.
DART is the first human mission to actively impact an asteroid, but it won't be the last. In April of this year, Wu Yanhua, deputy director of the China National Space Administration, said that my country will set up a near-Earth asteroid defense system, organize the preparation of a near-Earth asteroid defense development plan, develop a near-Earth asteroid defense simulation software and organize the basic process deduction. At the end of the "14th Five-Year Plan" period or in 2025 and 2026, a certain threatening asteroid will be carried out, both close observation and close impact will be carried out, and technical experiments will be carried out to change its orbit, so as to prepare for future human response to small asteroids. The threat of extraterrestrial celestial bodies to the earth's homeland has made China's new contribution.


