According to the Lunar Exploration and Aerospace Engineering Center of the National Space Administration, as of September 15, 2022, the Tianwen-1 orbiter has been in orbit for more than 780 days, and the rover has traveled 1,921 meters in total, completing the established scientific exploration tasks and obtaining primitive scientific Probe data 1480GB. The scientific research team has obtained rich scientific results through the research on the first-hand scientific data obtained independently by my country.

Through a comprehensive study of typical landforms such as concave cones, barrier craters, and trenches distributed in the landing area, the important connection between the formation of the above-mentioned landforms and water activities has been revealed.
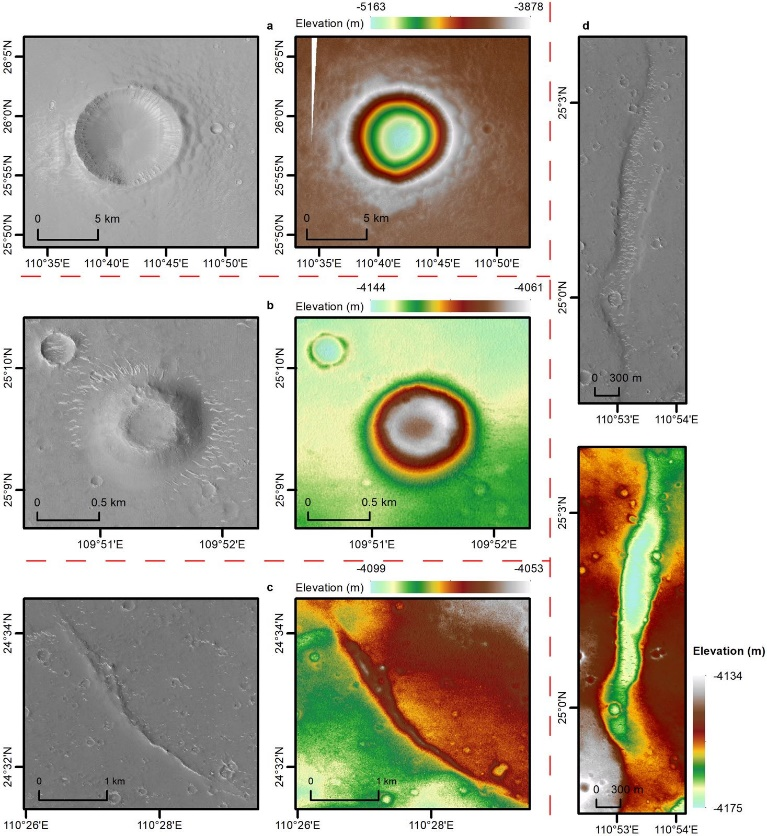
△Map of impact craters, concave cones, grooves and ridges in the landing area of Zhurong
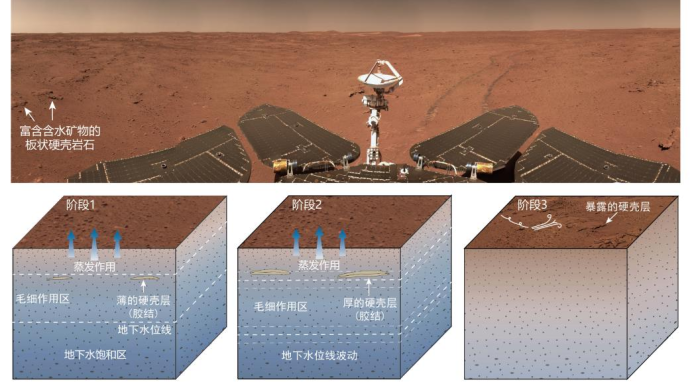
Through camera images and spectral data, hydrous minerals were found in plate-like hard-shell rocks near the landing area, proving that there has been a large amount of liquid water activity in the landing area since 1 billion years ago (late Amazonian period).
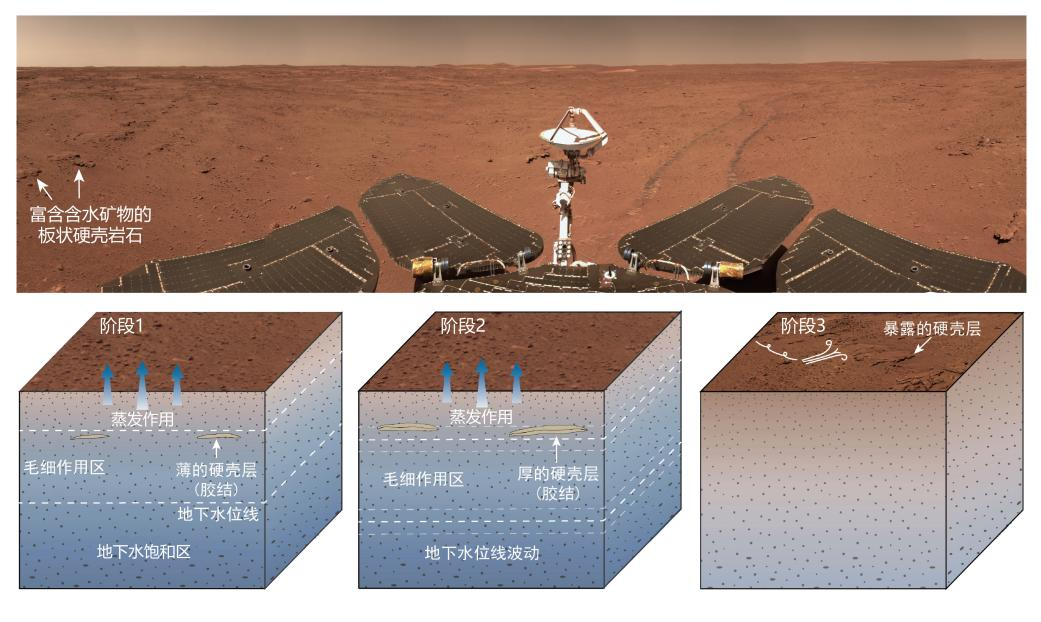
△ Schematic diagram of the plate-like hard-shell rock rich in water-bearing minerals found in the landing area by Zhurong and its formation process under the action of groundwater
Combined with camera images and rover moving ruts and other information, it is found that the soil in the landing area has strong compressive strength and low friction parameters, which are related to water activity and experience sand erosion.
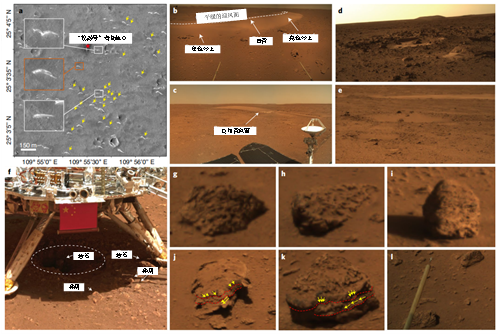
△Mars geological features and rocks in the Zhurong landing area
These new results reveal the impact of Martian sandstorm and water activities on geological evolution and environmental changes, provide strong support for the conjecture that there was an ocean in the Martian Utopian Plain, and enrich human scientific understanding of Martian geological evolution and environmental changes. The relevant results have been published in authoritative academic journals at home and abroad such as "Nature Astronomy", "Nature Geoscience", "Science Advances", "Science of China" and so on.
In addition, the scientific research team also used the detection data of Tianwen-1 to obtain a batch of data on the relationship between the density of rocks on the surface of Mars and the degree of surface erosion, the distribution of ions and neutral particles in the near-fire space environment, and the gravitational field of Mars. Excellent scientific results.
At present, the Tianwen-1 orbiter continues to carry out scientific exploration in the orbit of the remote sensing mission, continues to accumulate first-hand scientific data, and makes Chinese contributions to human beings' in-depth understanding of Mars.
