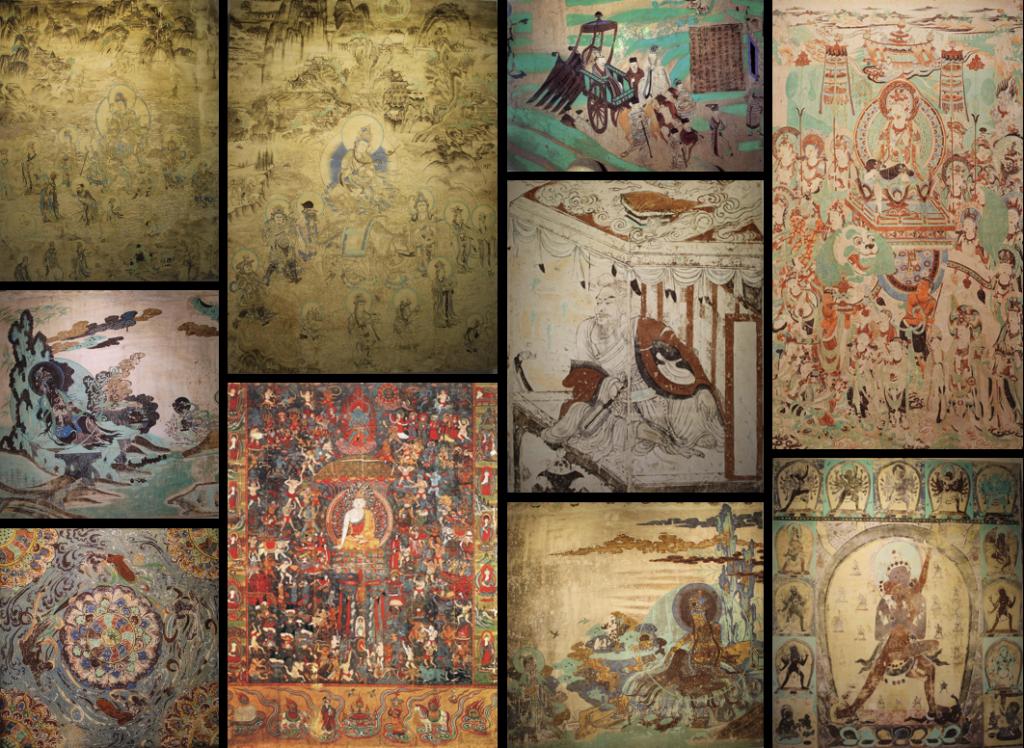

Dunhuang murals stored in DNA The pictures in this article are all from the official website of Tianjin University
The reporter learned from Tianjin University that the school's synthetic biology team innovated the DNA storage algorithm and stored ten selected Dunhuang murals in DNA. Through accelerated aging experiments, it was verified that the mural information can be stored for thousands of years at room temperature in the laboratory, and can be stored at 9.4 ℃. preserved for 20,000 years. The algorithm supports DNA molecules to become one of the most reliable data storage media in the world, which can preserve human cultural heritage information facing the crisis of aging and damage for thousands of years.
The results were recently published in Nature Communications.
The development of human civilization is closely related to the storage technology, from the knotted notes and Cangjie's characters to the modern magneto-optical storage technologies such as magnetic tapes and hard disks. With the advancement of science and technology, data storage methods continue to iterate and innovate. The team led by Yuan Yingjin, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Tianjin University, has been working on the next-generation storage technology - DNA storage. “According to the estimates of the International Data Corporation, the total amount of global data will reach a staggering 175ZB by 2025 (1ZB ≈ 10 to the 21st power byte). Data centers are being built all over the world, and the energy consumption of data centers is staggering. DNA storage Due to its characteristics of high storage density and low energy consumption, it is regarded as a potential storage technology and a new opportunity to meet the challenges of data storage growth," said Academician Yuan Yingjin.
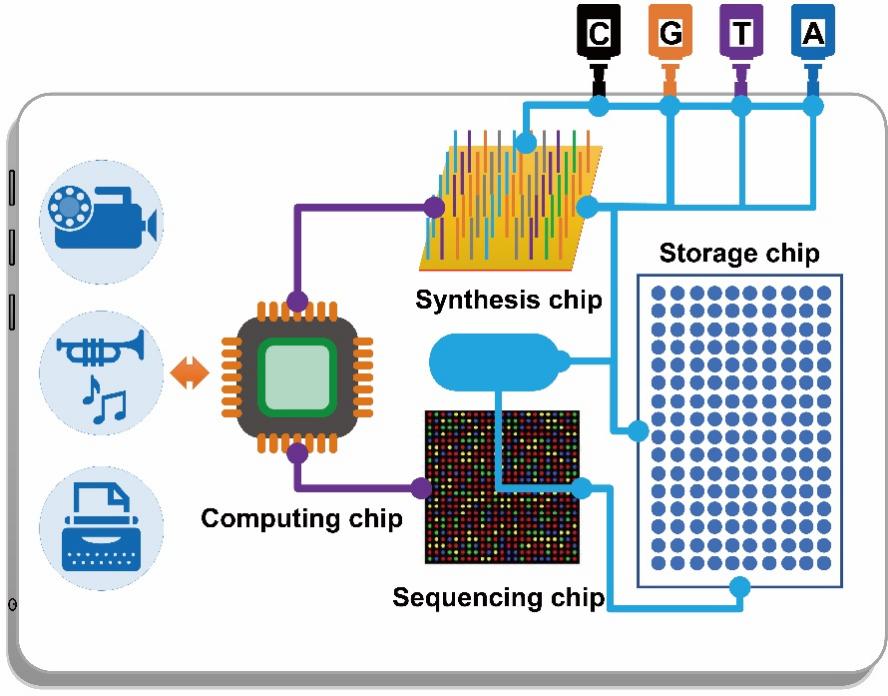
DNA storage technology conceptual diagram
In August 2021, Professor Yuan Yingjin's team made a major breakthrough in DNA storage, de novo coding and designing and synthesizing a yeast artificial chromosome with a length of 254886 base pairs dedicated to data storage, storing two classic pictures and a video on the artificial chromosome In this study, stable data replication was achieved by yeast propagation, and rapid data readout and error-free recovery were achieved by nanopore sequencing devices.
DNA storage is efficient and low-consumption, but as a chain biomacromolecule, it will face risks such as DNA breakage and degradation when stored in vitro at room temperature, which seriously affects the long-term reliability of information storage and is a key scientific problem to be solved urgently. In this regard, Yuan Yingjin's team designed a sequence reconstruction algorithm based on the Debreying graph theory to solve problems such as DNA breakage. The algorithm combines greedy path search and cyclic redundancy check code to achieve efficient de novo assembly of broken DNA fragments, which in principle supports the long-term reliability of DNA storage.
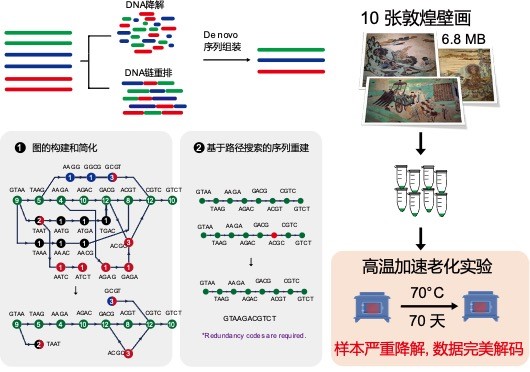
Sequence reconstruction algorithm designed based on Debreying graph theory to efficiently solve the problems of DNA breakage and degradation
Combining the sequence reconstruction algorithm (inner code) and fountain code algorithm (outer code), the team designed and encoded 6.8MB of Dunhuang murals, and synthesized 210,000 DNA fragments carrying picture information. For the long-term reliability of the data, the team prepared an aqueous DNA sample without any special protection, and accelerated the fragmentation and degradation of the sample at 70°C for up to ten weeks. More than 80% of the processed DNA fragments have breakage errors, and the designed sequence reconstruction algorithm can still accurately assemble and decode more than 96.4% of the fragments, and then use the fountain code to solve the problem of missing a small number of fragments, the original Dunhuang fresco pictures can still be Perfect recovery. According to theoretical calculations, this degree of high-temperature damage is equivalent to natural preservation at room temperature of 25°C for 1,000 years or 9.4°C for 20,000 years.
This is another important breakthrough made by the synthetic biology team of Tianjin University in the in vitro storage mode of DNA information after the breakthrough in the yeast in vivo information storage mode based on artificial chromosomes.




Comments