·This high-throughput analysis technology allows us to see for the first time how human immune cells cooperate collectively in a way that conforms to the laws of physics.  Elucidating the physical connection mechanism of cells in the human immune system has very important clinical research and application value, and can promote the diagnosis and prevention of many immune-related diseases such as infections, malignant tumors and autoimmune diseases. Progress, however, There has been a lack of clear understanding of its exact mechanism, and even some functional protein molecules on the surface of immune cells have not been able to find the corresponding ligand molecules, and have become so-called "orphan" receptors.
Elucidating the physical connection mechanism of cells in the human immune system has very important clinical research and application value, and can promote the diagnosis and prevention of many immune-related diseases such as infections, malignant tumors and autoimmune diseases. Progress, however, There has been a lack of clear understanding of its exact mechanism, and even some functional protein molecules on the surface of immune cells have not been able to find the corresponding ligand molecules, and have become so-called "orphan" receptors.
In the middle of the night of August 3, a research paper published online in the internationally renowned academic journal "Nature" showed that in order to elucidate the circuit diagram of the physical connection network of cells and molecules in the human immune system, scientists developed a method called "" Scalable Array Multivalent Extracellular Interaction Screening (SAVEXIS)" high-throughput microprotein interaction screening research technology, which can detect the interaction between molecules on the surface of immune cells at a scale close to whole-cell proteomics .
This method requires only trace amounts of protein molecules and can detect weaker interactions.
The composition of the human immune system is very complex, including immune organs, immune cells and immune molecules.
In order to perform a precise and effective immune response function, immune cells, as the main immune function performers, must continuously circulate in the body and redistribute in tissues, forming a dynamic and continuous physical contact network, and through its cells The protein molecules on the surface communicate, inhibit or activate the function of immune cells, and coordinate the immune system of the whole body to function. In order to comprehensively draw the detailed circuit diagram of the above physical functions, scientists have constructed a huge library of immune cell membrane protein molecules, which includes all CD molecules, all integrin family members, non-classical HLA molecules, VISTA and some other established molecules. The number of known "orphan" immune checkpoint molecules has reached 630 expressed protein molecules or combinations.
The results show that there are many unique pairing bindings between two protein molecules on the surface of immune cell membranes, such as the binding between integrins and other adhesion molecules, and the proportion of this situation is as high as 57%.
The interaction between immune cells is regulated by the physical interaction between protein molecules on the membrane surface. Many immune cell membrane receptors are "affinity switches that determine the function of leukocytes. The strength of their interaction with their ligands can determine the Transition of human immune cells between inflammatory and quiescent states.
Since immune cells are distributed across organs in the human body, their physical action diagrams can also reveal the multicellular network system of immune cell migration, activation and function execution in different organs and tumor tissue microenvironments, thus providing insights into different organs. Immunopathological processes of immune-related diseases and malignant tumors, providing precise information.
Not only that, but the research method also sheds new light on previous orphan receptor functions and their ligands, for example, the orphan receptor TNFRSF21 that universally activates T cell function.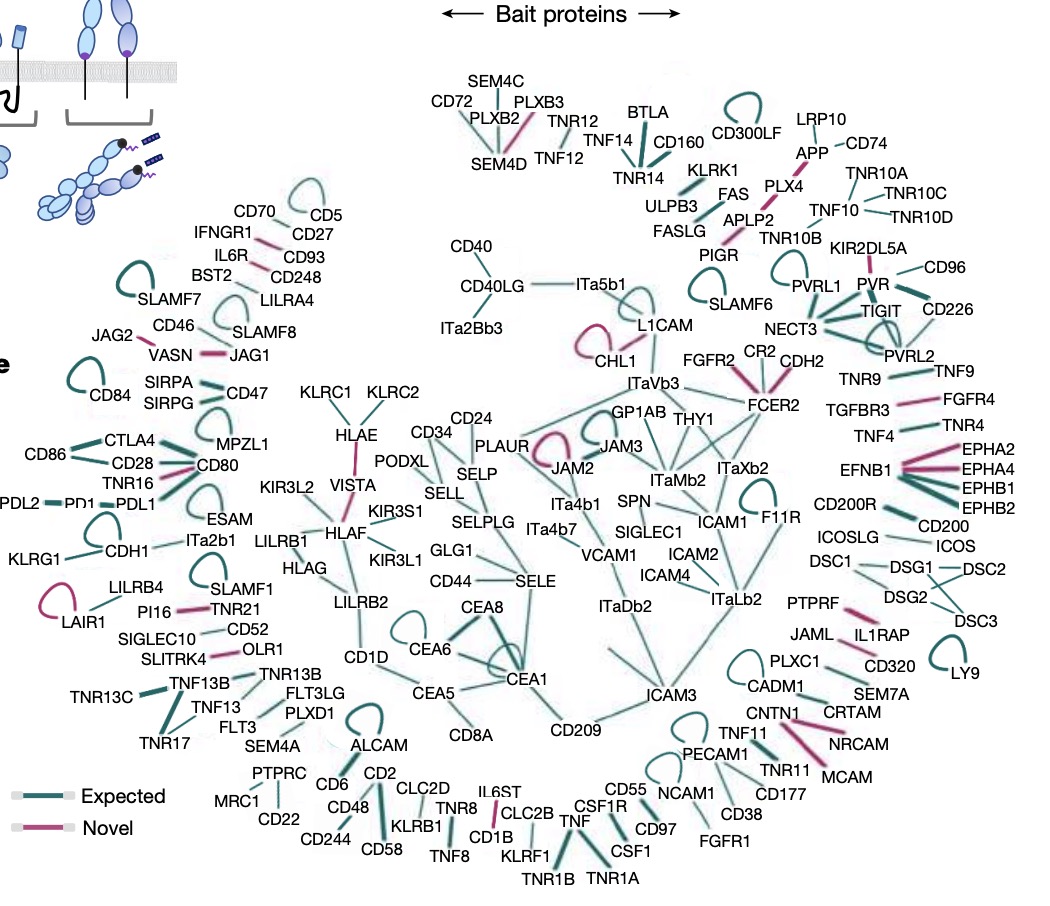
references
Jarrod Shilts, Yannik Severin, Francis Galaway, et al. A physical wiring diagram for the human immune system. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05028-x.
 Elucidating the physical connection mechanism of cells in the human immune system has very important clinical research and application value, and can promote the diagnosis and prevention of many immune-related diseases such as infections, malignant tumors and autoimmune diseases. Progress, however, There has been a lack of clear understanding of its exact mechanism, and even some functional protein molecules on the surface of immune cells have not been able to find the corresponding ligand molecules, and have become so-called "orphan" receptors.
Elucidating the physical connection mechanism of cells in the human immune system has very important clinical research and application value, and can promote the diagnosis and prevention of many immune-related diseases such as infections, malignant tumors and autoimmune diseases. Progress, however, There has been a lack of clear understanding of its exact mechanism, and even some functional protein molecules on the surface of immune cells have not been able to find the corresponding ligand molecules, and have become so-called "orphan" receptors.In the middle of the night of August 3, a research paper published online in the internationally renowned academic journal "Nature" showed that in order to elucidate the circuit diagram of the physical connection network of cells and molecules in the human immune system, scientists developed a method called "" Scalable Array Multivalent Extracellular Interaction Screening (SAVEXIS)" high-throughput microprotein interaction screening research technology, which can detect the interaction between molecules on the surface of immune cells at a scale close to whole-cell proteomics .
This method requires only trace amounts of protein molecules and can detect weaker interactions.
The composition of the human immune system is very complex, including immune organs, immune cells and immune molecules.
In order to perform a precise and effective immune response function, immune cells, as the main immune function performers, must continuously circulate in the body and redistribute in tissues, forming a dynamic and continuous physical contact network, and through its cells The protein molecules on the surface communicate, inhibit or activate the function of immune cells, and coordinate the immune system of the whole body to function. In order to comprehensively draw the detailed circuit diagram of the above physical functions, scientists have constructed a huge library of immune cell membrane protein molecules, which includes all CD molecules, all integrin family members, non-classical HLA molecules, VISTA and some other established molecules. The number of known "orphan" immune checkpoint molecules has reached 630 expressed protein molecules or combinations.
The results show that there are many unique pairing bindings between two protein molecules on the surface of immune cell membranes, such as the binding between integrins and other adhesion molecules, and the proportion of this situation is as high as 57%.
The interaction between immune cells is regulated by the physical interaction between protein molecules on the membrane surface. Many immune cell membrane receptors are "affinity switches that determine the function of leukocytes. The strength of their interaction with their ligands can determine the Transition of human immune cells between inflammatory and quiescent states.
Since immune cells are distributed across organs in the human body, their physical action diagrams can also reveal the multicellular network system of immune cell migration, activation and function execution in different organs and tumor tissue microenvironments, thus providing insights into different organs. Immunopathological processes of immune-related diseases and malignant tumors, providing precise information.
Not only that, but the research method also sheds new light on previous orphan receptor functions and their ligands, for example, the orphan receptor TNFRSF21 that universally activates T cell function.

The physical interaction between protein molecules on the surface of immune cell membranes. Green represents known interactions, red represents newly discovered interactions between molecules
The researchers believe that through the high-throughput analysis technology SAVEXIS, we have seen for the first time how human immune cells cooperate collectively in a way that conforms to the laws of physics . This also makes it possible to finally reveal the cellular physical connection of the immune system and other human physiological systems and the mechanisms by which they function.references
Jarrod Shilts, Yannik Severin, Francis Galaway, et al. A physical wiring diagram for the human immune system. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05028-x.



Comments